
What is Speed of Light? Details on Speed of Light
What is in this article?
If you are a lover of science fiction, you may be more familiar with the speed of light than anyone. Although spaceships moving at the speed of light with crews of hundreds of people seem like they remain science fiction only, they are still one of the topics people wonder about the most.
It is not possible for objects of any mass to reach the speed of light, which is the highest velocity that can be achieved in our universe. So don’t be disappointed when we say spaceships moving at the speed of light are only a dream; it is still possible to reach velocities that are quite close to the speed of light. Even though there are some obstacles (like the high amount of energy required) for travelling at a velocity close to the speed of light, it is still possible theoretically. Maybe this won’t be necessary at all and we can find a way to use the wormholes to travel in space.
While we keep watching scientific developments that are possible to happen, let us see the definition of the speed of light, which is the maximum attainable speed, and how it is calculated.
What is Speed of Light? How to Define it?
Speed of light is the movement speed of photons, which are particles of light. The speed that light has in space is exactly 299,792,458 meters per second. This corresponds to approximately 300,000 kilometers per second.
The highest speed attainable in universe, the speed of light is a universal constant. Speed of light is represented by a “c”, which stands for Constant, or Celeritas in Latin, translating to velocity. In the past, the letters c and V were used to symbolize the speed of light. In their study dated 1856, Wilhelm Eduard Weber and Rudolf Kohlrausch first used the symbol c to determine √ 2 times the speed of light.
In 1865, James Maxwell used the letter V for the speed of light while in 1894, Paul Drude used the letter c to directly refer to it. Einstein used V in his special relativity articles published in German but he preferred c in the following years.
What Does the Speed of Light Mean?
Although it sounds like a unit of time, the speed of light actually is a unit of distance. It is used to express the distance that light goes in a year. Light has a speed of around 300,000 km per second, which translates to approximately 10 trillion kilometers per year.
As we go short distances like only a few kilometers in our daily lives, it is pretty difficult for us to understand these values. Speed of light is often used by scientists to express the distance between heavenly bodies.
The Moon, stars and the Sun we see when we look up to the sky are actually the past versions of these heavenly bodies in speed of light. For example, it takes 8 minutes for sunbeams to reach the Earth. This means that a photon from the Sun goes eight seconds of light to reach the Earth. The moonlight, on the other hand, reaches the Earth in a second. In other words, it goes one second of light.
Who Discovered the Speed of Light? History of the Speed of Light
The interest of humanity in the speed and sped of light dates back to thousands of years ago. In 450 BC, Empedocles stated his views on the speed of light and in 525 AC, Anicius Boethius, a Roman mathematician, studied on the speed of light but he was blamed for witchcraft, which left his studies unfinished.
Various studies were performed and ideas were born on light through centuries but the speed of light was measured by Ole Roemer in 1676 for the first time. In 1670s, Roemer was working to create a reliable timeline for sea travel. In 1676, he observed eclipses of IO, the moon of Jupiter, and noted that the light has a certain speed. His calculations allowed him to notice that the time of eclipses changed as the distance between the Earth and Jupiter changed, and this happened in a certain order. Upon noticing that light travels in a measurable time, the speed of light that Roemer expressed was approximately 200,000 kilometers per second.
Although today we know that this number is not accurate at all, this study was an important discovery back then and caused the science world to focus on that direction. British physicist James Bradly took measurements and in 1728, he stated that the speed of light was 301.000 km/s, which is quite close to the actual value.
In, 1879, the speed of light measured by Albert A. Michelson was exactly 299,910 km/s. Considered the most correct measurement for long years, this value is quite close to the actual value.

How to Measure Speed of Light
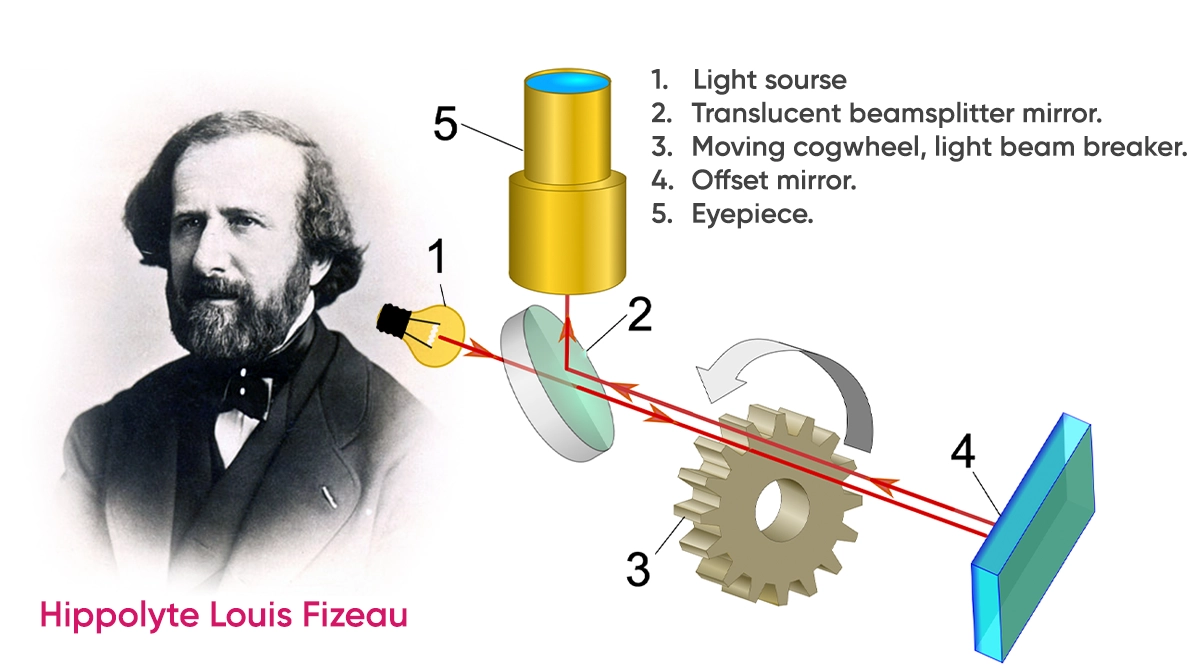 Throughout history, numerous methods were used to measure the speed of light. Ole Roemer tried to observe Jupiter and its moon IO to calculate the speed of light. In 1728’de James Bradley used the astronomical phenomenon known as the stellar drift to calculate the relative speed of light. In 1849,, Hippolyte Louis Fizeau used a mechanism comprising mirrors and a gearwheel to determine the speed of light. In 1862i Leon Foucault improved Fizeau’s work and used a system that was comprised of rotating mirrors. In this study, he found that the speed of light was 298,000,000 meters, which is quite close to the real value. He also stated that in water, light moves more slowly than air.
Throughout history, numerous methods were used to measure the speed of light. Ole Roemer tried to observe Jupiter and its moon IO to calculate the speed of light. In 1728’de James Bradley used the astronomical phenomenon known as the stellar drift to calculate the relative speed of light. In 1849,, Hippolyte Louis Fizeau used a mechanism comprising mirrors and a gearwheel to determine the speed of light. In 1862i Leon Foucault improved Fizeau’s work and used a system that was comprised of rotating mirrors. In this study, he found that the speed of light was 298,000,000 meters, which is quite close to the real value. He also stated that in water, light moves more slowly than air.
In the following years, when the relationship between light and magnetism was revealed, more modern methods were developed to measure the speed of light. In 1907, Rosa and Dorsey used magnetic permeability and electric permeability constants to calculate the speed of light, which yielded a result that was approximately 299,788 km/s. In 1958, Froome used the interferometer which utilized radio waves and visible light, as a result of which he calculated a speed of light of 299,972,500 m/s. In 1972, Evenson revised Froome’s experiment using lasers and interferometers to measure the wavelength of light. The speed of light he found was 299,972,456 m/s. In the same year, a group of scientists at the USA National Bureau of Standards measured the speed of light in space as 299,792,456.2 m/s.
Does Speed of Light Have a Constant Value?
The speed of light in space is exactly 299,792,458 meters per second. This is the maximum velocity that light can reach. In different environments, light can move at lower speeds. It shows both wave and particle properties. When light is considered a particle, each particle is called a photon. When light moves in a different environment like water or air, the molecules in that environment cut down the speed of photons.
When we review light in terms of its wave properties, we can see that it is comprised of electromagnetic waves. Because of this property, other electromagnetic waves in the environment cause the speed to slow down.
Speed of Light and Physics
 The most important one of the studies that helped us understand the speed of light is the special relativity, or the theory of relativity, which Albert Einstein put forward in 1905. The theory of relativity explains the behavior of matter at the macroscale while also functioning as a solid basis to explain the universe and how it operates.
The most important one of the studies that helped us understand the speed of light is the special relativity, or the theory of relativity, which Albert Einstein put forward in 1905. The theory of relativity explains the behavior of matter at the macroscale while also functioning as a solid basis to explain the universe and how it operates.
E = mc² is the equation that often represents the theory of special relativity, which explains the effects of speed on mass, time and space. In this formula, E stands for energy, m for mass and c for speed of light.
This theory by Einstein got the science world to question many things they thought they knew. What makes this theory is so important is that as science has improved, Einstein’s predictions have been confirmed numerous times.
The basis of the theory of relativity is that any matter can travel at speeds that is close to that of light but it can never reach or exceed it. According to this theory, as the speed of a matter increases, its mass increases as well. Based on this view and considering the fact that the matter has a certain mass and this mass increases as speed does, the mass is expected to increase as the matter gets close to the speed of light. An infinite energy is needed to get the matter to the speed of light. As no such energy exists, it is not possible to reach the speed of light.
The fact that photons traveling at the speed of light are massless particles, explain how they move at the speed of light based on this formula. In experiments by scientists, it was made possible for light particles such as protons to travel at velocities that are very close to the speed of light. However, the speed of light cannot be attained. Although in theory, it is possible for objects with a larger mass to travel at velocities close to the speed of light, it does not seem very possible in practice with today’s technology.
Below are Einstein’s assumptions regarding space-time and the speed of light as well as his Theory of Relativity:
- Speed of light is the speed limit of our universe. The highest speed that can be attained is that of light. It is impossible to exceed the speed of light.
- The speed of light is measured in the same way by every observer.
- As matter accelerates, time starts to flow more slowly for it. Accordingly, it is expected that when the speed of time is reached, time will stop for that matter.
- Space and time are interrelated concepts. For this reason, the flow of time varies depending on the locations of observers relative to one another.
- As the speed of an object increases, its length decreases in line with the movement.
- Rest mass belongs to the object itself and resist to acceleration. Accelerated object lose some of its mass and this mass is converted into kinetic energy. An object must not have a rest mass in order to reach the speed of light.
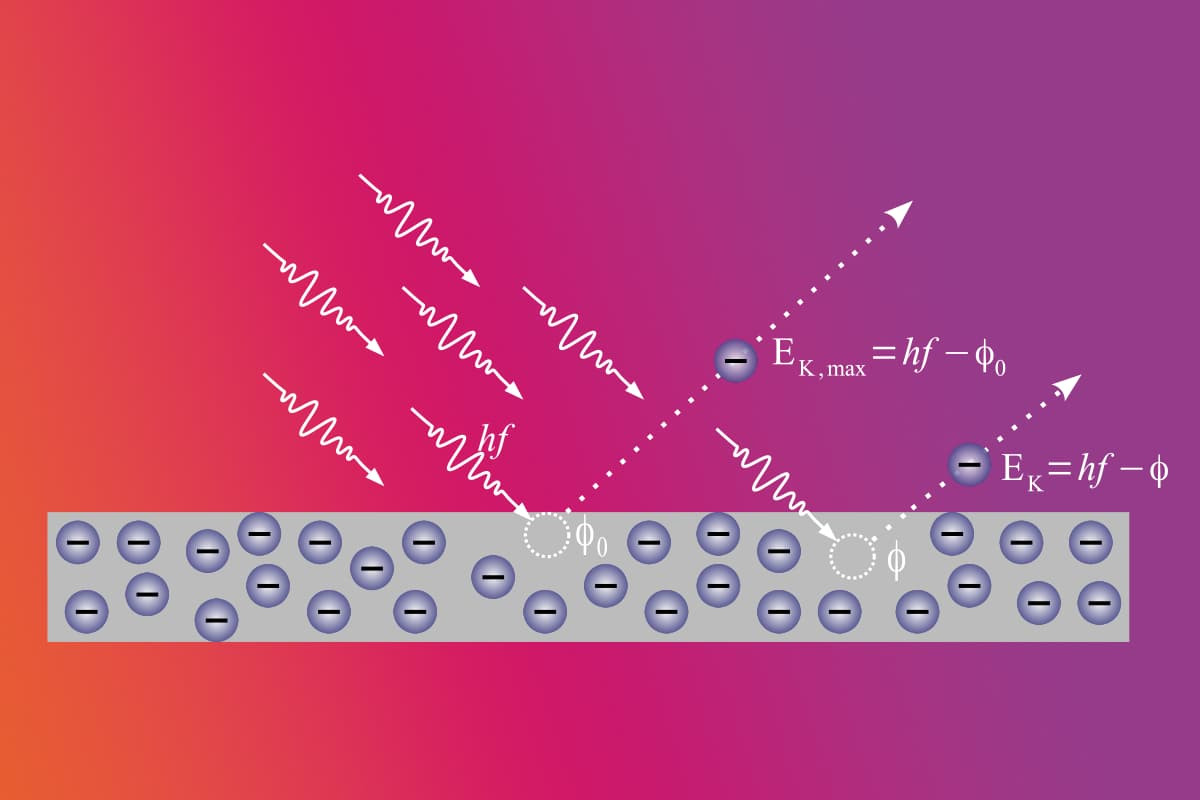
In addition to his theory of relativity, Einstein, in his studies on photons, also explained the photoelectric effect explaining that the light energy is quantized as photons, which contributed to the quantum mechanics.
Speed of Light Today and Relevant Research
It is acknowledged by the science world that the speed of light is constant and it is impossible to reach or exceed it. However, this does not stop scientists from conducting studies on light and the speed of light. In the past, studies on light allowed for discoveries such as the photoelectric effect and today, studies are still being performed on the behavior of photons.
For example, Scottish scientists conducted studies in 2015 and managed to slow down the photons traveling in space. Studies are now underway to use photons more effectively especially in data transmission due to their speed. Relativity communications studies are being performed for communication with space vehicles that travel at velocities close to the speed of light. Another study is for allowing the matter to get superconductivity through photons. When we talk about velocities that are impossible to attain and hard to understand, such as the speed of light, there are numerous questions to answer. We answered the most popular questions about the speed of light for you.
Is It Possible to Exceed the Speed of Light?
It is not possible to exceed the speed of light. Speed of light is a value that is the limit of attainable speed in our universe. As Einstein stated in his theory of relativity, a matter must have no mass in order to reach the speed of light, or infinite energy is needed to get a matter with a mass to the speed of light. As both scenarios are impossible, it is unthinkable to exceed the speed of light.
What is the Closest Speed Attained to the Speed of Light?
Although it is not possible to reach the speed of light, experiments allowed to obtained protons that move at velocities that are quite close to the speed of light. The Large Hadron Collider (LHC) at CERN accelerates protons by 99,9999991% of the light of speed.
What is the Relationship Between the Speed of Light and Internet Speed?
Fiber optic cables are used to ensure intercontinental connection for the internet, which can be defined as a network of computers covering majority of the world. Today, fiber optic cables are used even in domestic internet connection. These cables benefit from light for data transmission. This allows data transmission to reach very high levels.
Even though we cannot reach the speed of light, which is the highest speed attainable in universe, don’t you find it interesting that it is used in daily life such as in fiber optic cables? Don’t forget to share your thoughts with us.
Even though we cannot reach the speed of light, which is the highest speed attainable in universe, don’t you find it interesting that it is used in daily life such as in fiber optic cables? Don’t forget to share your thoughts with us.

 Online Services
Online Services Application Inquiry
Application Inquiry Pay Assurance Fee
Pay Assurance Fee Query Installation Number
Query Installation Number Compensation Fee Inquiry
Compensation Fee Inquiry Automatic Payment Order Inquiry
Automatic Payment Order Inquiry Partnership
Partnership



Leave a Comment