
What Is a Lightning Rod? How Does It Work? Vitality of a Lightning Rod
What is in this article?
Lightning rod systems are one of the effective mechanisms that prevent potential tangible and intangible losses caused by a lightning originating from the interaction between the sky and the earth due to adverse weather conditions.
The magnetic field that perpetually exists between the sky and the earth produces lightning currents due to electrifications released under the changing atmospheric conditions. If the discharge power produced by a lightning is transmitted into the ground in a controlled way with the help of a Lightning Rod, this will prevent the damages caused by lightning currents with very high intensity.
In the rest of our blog content, you can find all the details about a lightning rod that prevents major damages, such as loss of life and property, caused by a lightning strike.
What Is a Lightning Rod Classified as a Surge Arrester and What Does It Do?
The world's atmosphere accommodates electrical charges that are presumed to be caused by depending on the planetary rotation speed. Additionally, the magnetic air flow that is thought to be caused by different factors leads to a number of natural phenomena.
On the other hand, electrical charges caused by the combination of some factors, such as temperature, wind, rain and cloud, under favorable conditions are drawn to the ground with the help of the supply earth (physical existence of the ground that makes up the earth and consists of an object or matter).
A lightning rod is a kind of grounding system that prevents the lightning strike risk. It is an effective mechanism that fends off unwanted electrical charges into the ground in a controlled and safe system. It is used on ships and in industrial plants and at heights that are likely to be damaged by electric currents in the air, especially high-rise buildings and skyscrapers.
A lightning rod eliminates the potential hazards from high-current electrical energy released in the magnetic field under atmospheric conditions. Surge arrester devices ensure that a heavy electric current referred to as a lightning strike descends to the ground safely.
It is very likely that there will be a short circuit in various electrical appliances, electrical panels or central electric units in buildings, facilities or plants after a lightning strike. A grounding system that engages before the said adverse conditions arise serves to protect both people and equipment from lightning damage against the risks of fire, loss and death.
How Does a Lightning Rod Known for Arresting Lightning Work?
 The methods of protection from damage caused by lightning are divided into two groups; lightning preventers and lightning arresters. Lightning rods work based on the principle of arresting lightning. Installed at the highest point of the intended structures and also called as the external lightning protection system, lightning rods attract the lightning and deliver the current to the ground with the help of a metal rod at the tip.
The methods of protection from damage caused by lightning are divided into two groups; lightning preventers and lightning arresters. Lightning rods work based on the principle of arresting lightning. Installed at the highest point of the intended structures and also called as the external lightning protection system, lightning rods attract the lightning and deliver the current to the ground with the help of a metal rod at the tip.
Located at the highest part of buildings or high places, lightning rods consist of a long and pointed pipe, a metal plate buried underground and copper conducting wires connecting the two assemblies. The structure of conducting wires and the ions at the end of these wires arrest the static electric current released due to the collision of clouds. The current transferred to the ground through conducting wires is neutralized by the neutralizing property of the ground.
It is mandatory to have the periodic maintenance, which is stipulated by legal requirements with the support of the Ministry of Labor and Social Security, carried out at least once a year. During the lightning rod periodic inspection procedures, the system is checked for proper functioning with the help of measuring devices.
The pole and its arrester tip are checked for any corrosion. Down conductors are checked for descending by maintaining the S distance. The S distance, which is called the safety distance, is the protection allowance that sends the electric current to the earth in a safe and controlled way during a lightning strike. To put it more clearly, it is the safety margin that allows for no sparking jump throughout the copper wire assembly with a down conductor until it reaches the closest grounded conductor (metal plate buried underground). A continuity test is conducted on down conductors. Measuring terminal blocks are replaced or crimped.
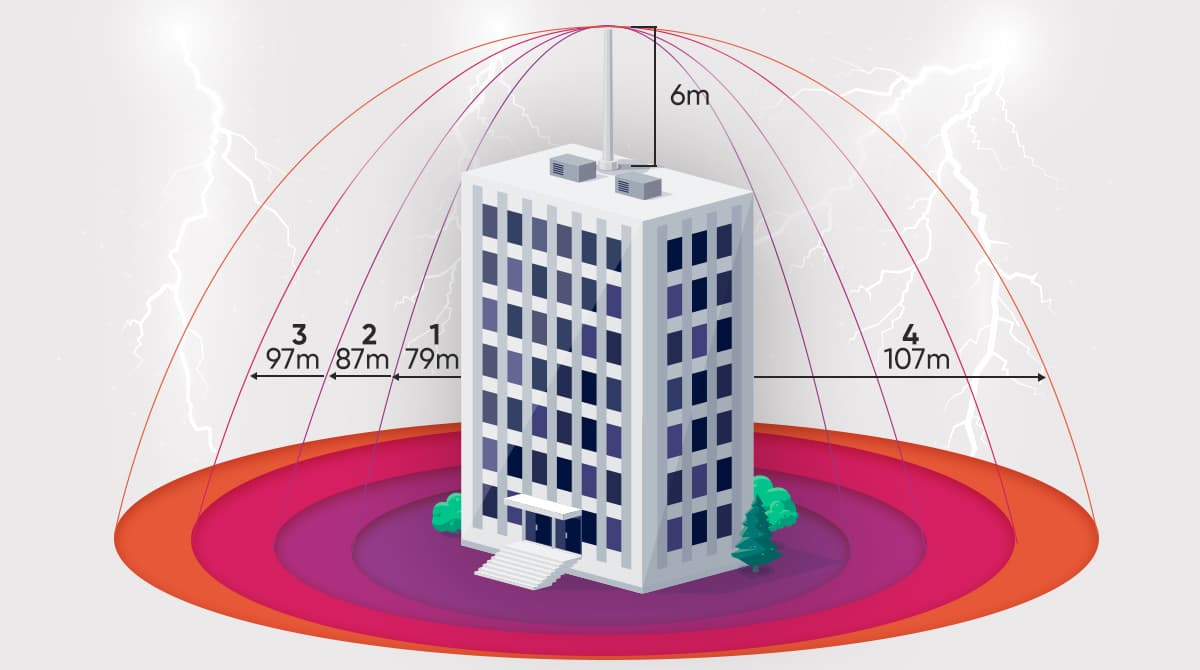
How Large Is the Area Covered by a Lightning Rod Transmitting the Lightning Safely to the Ground?
A lightning risk assessment is carried out using specific methods for every area that needs to be protected from the lightning strike risk. This establishes both in which level of risk category the building or the area is included regarding the determination of the covered area and how many meters are needed for the lightning rod protection diameter.
This is performed by electrical engineers using software programs that are of high accuracy and validity standards. It is very important to calculate until which distance lightning arresters will provide a protection zone. In any case falling within the area of expertise of those engineers carrying out the project design, it is required calculate the intensity and angle of the electric current striking the area subject to a possible lightning.
One of the most important criteria to consider in lightning level calculations is the knowledge of which risk category the lightning protection level falls within. Based on the most accurate calculations made under conditions suitable for the analysis standard IEC 62305, lightning protection zones are divided into four different levels:
-
Level 1
This is the highest risk level and includes lightning strikes with a current rating up to 200kA. While the probability of such heavy lightning strikes in our country is at a minimum level, the hazard class of petrochemical plants in high risk zones is very high. The lightning rod protection zone determined based on the table with the highest risk of lightning strikes has a radius of 79m.
-
Level 2
This level includes the lightning strikes in high risk zones, with a current rating up to 150kA. Provinces like Aydın, Antalya, Burdur and Mersin are exposed to strong pulses caused by a lightning strike. The area covered by a lightning rod used for the protection of industrial facilities, hospitals and factories in provinces in level 2 risk group should be 87 meters in radius.
-
Level 3
This is the level that covers lightning strikes that produce a current rating of 100kA, while it applies to structures and high places that fall within the standard risk category. A Level 3 lightning protection zone requires the protection of an area with a radius of 97m. Many parts of Turkey are in this risk zone. For this reason, the lightning rod system that provides a lightning protection zone is used in all industrial facilities, especially in high risk places such as hospitals, factories and mosques.
-
Level 4
The Level 4 risk category that includes the probability of a lightning strike is in the low risk group and covers the protection of an area that measures 107 m in radius. An appropriately designed product should be used since calculations made based on the values of the descent angle as well as the intensity of a lightning strike reveal the need for protection from low risk lightning.
When Was the Lightning Rod Preventing Lightning Strikes Used First?
The renowned scientist Benjamin Franklin managed to identify and name electrical charges as positive and negative in line with the results of a range of experiments he conducted. Concluding that electricity is in liquid state upon his studies, the inventor determined that the force existing in certain environments is present in insufficient or excessive amounts. Franklin, who argued that objects repel each other in the case of excess or lack of the electrical power within them, asserted that objects with excess electrical power in one and deficient electrical power in the other also attract each other. As a result of analyses from experiments, he named the current potential with an excess of charge as positive and the values that could be measured as a deficit as negative.
Maintaining his experiments by using a Leiden jar that stores electricity, the well-known scientist observed the effects of thunder and lightning that may occur in connection with the storm. As he progressed, he observed that the electricity in the Leiden jar was discharged by producing both sparking and crackling sound, noticing that the two were correlated. Franklin managed to invent the lightning rod, succeeding in charging the electricity into the Leiden jar thanks to his kite experiment during a stormy day in 1752.
Making the first lightning rod in 1760, Benjamin Franklin used a pointed iron rod that consisted of a very simple assembly. The renowned inventor, who was connecting the end of the iron rod to the ground, started to use a platinum rod instead of the iron rod in the following periods.
From 1782, the number of lightning rods that started to be common in residential buildings in the state of Philadelphia, U.S. exceeded 400. Lightning rods, which were developed in different sizes and with different properties in the following years, provided protection from the lightning current on ships as well as in high-rise and low-rise buildings.
Who Invented the Lightning Rod?
The lightning rod, namely the lightning arrester, was invented in 1752 by Benjamin Franklin who was known as a polymath and scientist. After a large number of experiments he carried out, Franklin discovered that lightning is a variety of static electric current. Finding out that opposite poles attract each other, the inventor then invented the lightning rods and managed to prevent major damages caused by lightning. Some varieties of lightning rods were started to be used throughout the United States after 1782.
The Faraday cage, invented and named after the British Physicist Michael Faraday (1791-1867), is a mesh-shaped lightning protection unit that is coated or plaited with the electrical conductivity of metal.
Radioactive lightning rods were invented and introduced to the science world after studies and experiments carried out on radioactive substances by physicists such as Marie Curie (1867-1934) from Poland and Hungarian-American Leo Szilard (1898-1934).
Additionally, active lightning rod systems, which have been extensively used as one of the new discoveries of the age and which is trusted due to their radiation-free composition, have been invented a short while ago.
What Are the Types of Lightning Rods Preventing Lightning Risks?
The types of lightning rods are categorized based on both their properties and impact zones. Divided into four – active lightning rods, radioactive lightning rods, Franklin's lightning rod and Faraday cage, lightning arresters are currently used mostly in the form of Franklin's lightning rod and Faraday cage. These could be listed as follows:
Franklin's Lightning Rod: The Franklin's lightning rod, which consists of rods (Air terminals), conducting wires and long and thick ground rods, is used to protect high-rise buildings, as well as high places at risk, from lightning damage.
Faraday Cage: The lightning rods given the form of a cage, which are used to protect from lightning any low-rise structures that have no tall buildings and sharp protrusions around, are called Faraday cages.
Radioactive Lightning Rods: The lightning protection system, which helps the lightning descend to the ground through a safe and controlled path, serves to provide protection thanks to the ion elements they emit into the air.
Active Lightning Rods: The options that produce an early flow warning effect by becoming active according to the changes in weather phenomena create a circular protection zone as they arrest static electrical charges accumulated in the air and convey them to the ground.
Where Are Vital Current Arresting Lightning Rods Used?
 The mandatory use of lightning rod systems that provide protection from heavy static electrical power caused by lightning is set forth within the scope of the Regulation on Fire Protection of Buildings governed by the Ministry of Interior and the Ministry of Housing. As per the Planned Areas Zoning Regulation, article 53, paragraph 1: “Any places that contain explosives and pointed and high-rise buildings and facilities must be equipped with a lightning rod in accordance with TSE standards pursuant to the Regulation on Fire Protection of Buildings.”
The mandatory use of lightning rod systems that provide protection from heavy static electrical power caused by lightning is set forth within the scope of the Regulation on Fire Protection of Buildings governed by the Ministry of Interior and the Ministry of Housing. As per the Planned Areas Zoning Regulation, article 53, paragraph 1: “Any places that contain explosives and pointed and high-rise buildings and facilities must be equipped with a lightning rod in accordance with TSE standards pursuant to the Regulation on Fire Protection of Buildings.”
In this case, lightning arresters should be used in facilities that are at high risk of damage and loss of life and property and in buildings with a eaves height exceeding 30.5 m as well as mosque domes and ships. Lightning rods that are also an effective grounding system beyond being mandatory are vital as a kind of measure of protection from fire.
The Faraday Cage is preferred where protection from fire risk is not possible through a lightning rod. The intended uses of a Faraday Cage that is installed with metal sheets plaited or metal materials coated are given below:
- Devices emitting radio frequency, such as medical and industrial machinery,
- Warehouses containing inflammable or explosive materials,
- Buildings where radio communication is used, such as police units and factories,
- Radio frequency modules which fulfill the function of electronic cards and which are needed in places where identity recognition systems are used or electronic fund transactions take place, and
- For social purposes - places where the Internet should be disconnected.
It is not suitable to use lightning rods when buildings, high places and equipment are made or built of mostly metal. It is also not suitable to use lightning arrester equipment for tower cranes, base station towers, wind power plants and TV and radio transmitter towers that are predominated by metal materials attracting lightning.
How to Install a High Quality Lightning Rod with a Functional Design in Buildings
Lightning rods are installed at the highest point of buildings or at the top of pointed structures. In addition, lightning protection equipment should be positioned at 1.5 m height from the point of installation. The arrester rod should be in a pointed form made of stainless steel with a length of 50 cm and a cross section of 16 mm2. The body pole made of galvanized pipe should be ideally 6 m long and fixed to a suitable point, such as a wall or roof, using a clamp.
The convenient edges should be preferred for the lightning rods that are to be mounted onto large and even buildings, while an installation layout with a spacing of 15 m should be followed. Copper wires that allow a grounding system to work effective and reliably should both be 95% pure and have the properties of electrolytic copper. This produces the maximum conductivity potential that creates a suitable environment for the lightning arrester to arrest a heavy electric current and send it to the ground.
The lightning rod, which is installed by efforts requiring expertise, encompasses the whole of coordinated activities before mounting. It is important that people, who are knowledgeable about and have practical experience in all applications such as electrical grounding along with the electrical installation system, are assigned in the installation phase.
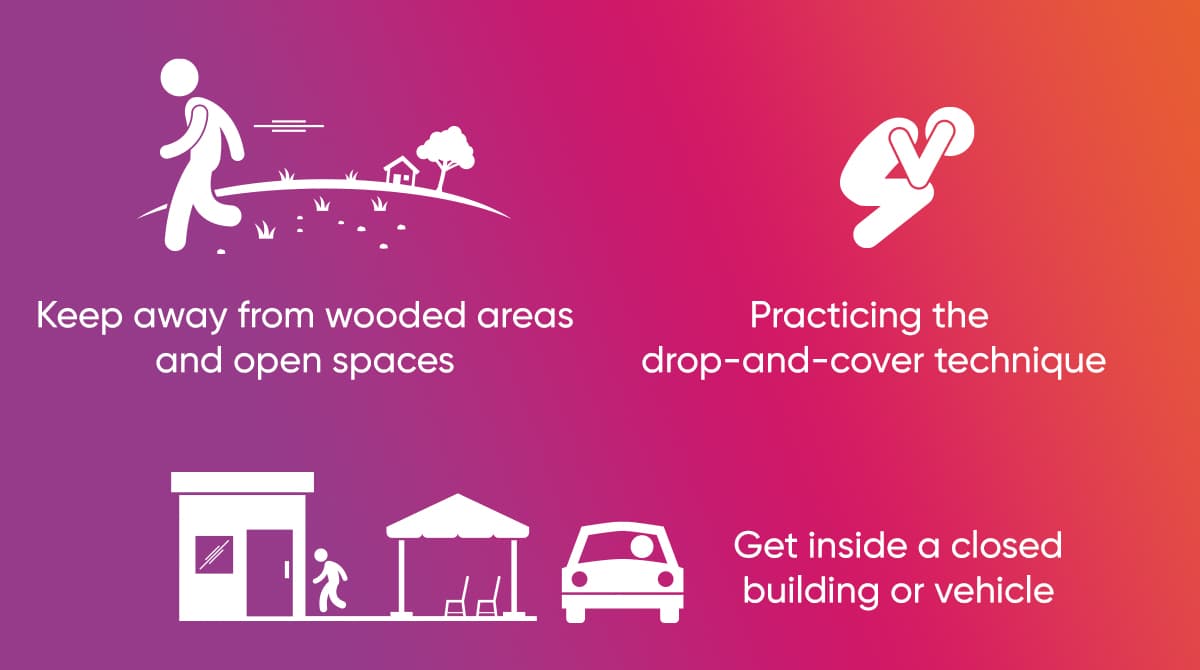
10 Most Effective Basic Rules of Lightning Protection
Different methods of protection from lightning hazards can be lifesaving with the measures that are extensively reported by the Disaster and Emergency Management Presidency. You may consider the suggestions given below should you be likely to be exposed to lightning strikes when you are inside a building, in an open field or outdoors:
- You can take shelter in a building or under a covered tree or use the drop-cover-hold on tactic if there is no such possibility.
- It is important to stay clear from woodlands and exposed areas during a severe storm.
- Those who are outdoors at the time of noticing a possibility of lightning strike should go inside a closed building or vehicle.
- In case of sensing the risk of a lightning strike; doors and windows should be closed tightly, and curtains and blinds should be pulled.
- Some signs, such as electrification in the hair and tingling or crackling when in the open field, are the indications that there is an increased probability of lightning strikes.
- You should to go to the lowest part of open fields where there is no place to take shelter, drop yourself on the ground and put your feet together and cover yourself touching the ground on your tiptoe and hiding your head between your knees.
- In even and high places, it is advisable to keep your head low, avoid voltage difference by putting your feet together and reduce contact with ground and refrain from taking a lying or reclining position on the ground under any circumstances.
- It is likely that lightning strikes the same place more than once.
- Lightning can strike areas 15 to 20km away from the precipitation area.
- While rubber slippers and shoes do not provide lightning protection, you can avoid coming into contact with metal and touch hard places such as wood and walls.
What was the most interesting point about lightning rods? Now it's your turn to take the floor on the Lightning Rod, a crucial invention! You can share your thoughts in the comments.

 Online Services
Online Services Application Inquiry
Application Inquiry Pay Assurance Fee
Pay Assurance Fee Query Installation Number
Query Installation Number Compensation Fee Inquiry
Compensation Fee Inquiry Automatic Payment Order Inquiry
Automatic Payment Order Inquiry Partnership
Partnership





Leave a Comment