
What is in this article?
Rapid advance of technology has made electricity an indispensable component in every aspect of life. In addition to places such as houses, schools and cafés, electricity has been accessible even in mass transportation vehicles in recent years. There are some points to watch out for when using electricity that is used so frequently and needed almost at any time.
Turning into a hazardous energy source when not used properly, electricity can harm human body severely. Any person exposed to electric current may have their body burned or have their vital organs such as heart damaged. Thus, every individual needs to be self-aware of electricity to avoid such hazards.
What are the effects of electric current on human body? How should a person injured due to electric current be responded to? Let's go through the points to consider when using electricity together with the answers to these questions.
What Is Electric Current?
To understand the effects of electric current on human body, it is first required to analyze how electricity works. Electric current is the name given to the travel of electrons from negative to positive in a conductive material such as metal wire. In other words, it is the flow of an electrical load. The unit used to measure electric current is ampere.
Ampere can be compared to the water flowing through a hose. For example, pressure is needed for the water to flow through the hose when hosing a garden. Likewise, a similar intensity is required for electric current to run through wires. On the other hand, human body is electrically conductive and draws intense current. Therefore, electric current can cause very severe damage to human body.
More often than not, electricity is considered to be non-hazardous as it maximizes the comfort of daily life through its utilization in every field and facilitates life for being accessible to individuals from all ages. For security, however, one should always take into account how severe hazards this energy source can lead to. It is possible to be exposed to electrical issues and hazards at any time at home, work or school where powered devices are used.
Electric shock is the rapid excitation of the nervous system as electric current runs through the body. Holding two wires with different voltage rating at the same time or coming into contact with the ground concurrently while holding a live wire may result in electric shock. In addition, holding two wires with the same voltage rating at the same time poses a risk as well. This is because one of the wires is likely to be negatively charged, while the other is likely to be positively charged. If this is the case, electric shock might occur despite no contact with the ground.
Additionally, touching an electrocuted person might also lead to electric shock. The person may feel pain or get injured due to electric shock. Although it often results in pain, internal organs are not always damaged. The body parts where electricity goes in and out are damaged. In addition, the tissues on the path it travels in the body are also damaged.
Injuries Caused by Electric Currents
Exposure to electric current may cause various health issues for a person. Internal bleeding may develop; the person may suffer nerve, muscle or organ loss. These issues include burns, irregular heartbeat, tingling sensation, loss of consciousness and headache.
While, on the other hand, some people are not exposed to bodily injury, some may feel severe pain or suffer tissue damage. If a person is exposed to prolonged high current, they may be at risk of some conditions, such as heart attack, cardiac or respiratory arrest. The person who survives electric current may even die subsequently since it produces many latent effects.
Electric shock may also lead to various health issues in the long term. It is likely to be exposed to neurological, psychological and physical conditions. Potential psychological issues that follow electric shock include post-traumatic stress disorder, depression, anxiety, insomnia, concentration difficulties and panic attacks.
On the other hand, the likely neurological conditions are memory and balance loss, fainting and sciatica. Alternatively, a person may experience some physical health issues, such as headache, fatigue, muscle spasm, joint stiffness and night sweats. Injuries or fractures may also occur due to the reactions given when exposed to a current even if it is very small.
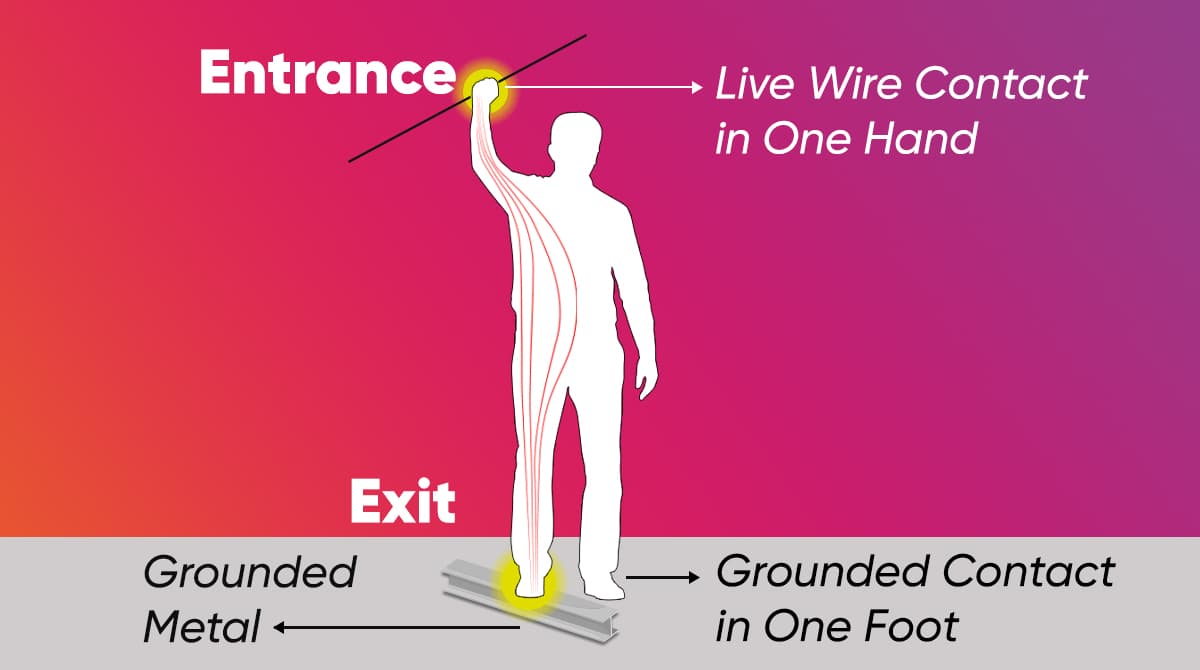
What Happens if the Live Wire is Not Released in an Electrical Accident?
A person who has had an electrical accident may not be able to release the live wire. This is because electric currents cause spasm in muscles. Currents at a frequency of 50 Hertz and ranging between 10 and 40 milliamperes lead to tetanic spasm in skeletal muscles. If a current has entered the body through the hand, flexor muscles that allow the fingers to bend inward will make the hand closed and grasp any object in the palm firmly due to a tetanic spasm.
If, consequently, a tetanic spasm has developed, the person exposed to electric current may not manage to release the tool or wire they are holding, even if they want to. If this is the case, the electrical circuit remains switched off, increasing the degree of injury. The risk of skin burns and cardiac complications also increase. Based on the studies, 220V mains electricity at a frequency of 50Hz causes a firm grip on the object in the palm of women due to muscle spasm when over 6 milliamperes and in the palm of men when over 9 milliamperes.
5 Factors Affecting the Damage in Case of Electric Shock
There are various elements that affect the damage caused to the body by electric shock. The longer a person is exposed to electric current, the greater the damage will be. The most important factors affecting the damage in case of electric shock are:
-
Duration of Electric Shock
How long a person is exposed to the current is highly important regarding the effect of the current. The longer the current travels through tissues, the greater damage it causes. In addition, the likelihood of death increases. Even a current as low as 12 volts, which is considered non-hazardous, may result in death in case of prolonged exposure. Additionally, the length of the duration of electric shock greatly increases the severity of thermal burns in the event of higher voltages.
-
Type of Current
The type of current is the other factor that affects the damage caused by electric shock. Comparing the types of current that are divided into alternating current (AC) or direct current (DC), AC, which is the mains current used in homes and industrial establishments, is more dangerous than DC. This is because alternating current often causes irregular heartbeat. In addition, many parts of the body are more susceptible to alternating current.
Considering the damage caused to the body by alternating current and direct current, it is easily discernible that alternating current is more dangerous. Sudden cardiac arrest may occur when exposed to an alternating current of 100 milliamperes for a period as short as one-fifth of a second. However, exposure to a direct current of 250 milliamperes for one-fifth of a second will not cause death.
-
Voltage
The voltage of an electric current also affects the size of electric shock. As set forth in the Electrical Internal Installations Regulation, the voltage that is dangerous for the human body is the voltage with an effective value above 50 Volts. The damage sustained is affected by whether the voltage is low or high. High voltage is considered more dangerous than low voltage, but one cannot say that low voltage also poses no risk.
When the voltage is low, the path of transmission is the circulatory system. In other words, current passes over the heart. Consequently, low voltages may also cause shock, leading to potential death. In the event of high voltage, many organs in the circulatory system become conductive as the body is exposed to more electricity. High voltage can usually be accompanied by tissue burns due to overheating.
-
Current Intensity
The other key factor that affects the damage caused by electric shock is the intensity of a current. The damage sustained considerably increases as the current intensity increases. That being said, the current intensity decreases and mitigates the hazard when the resistance is high, while the current intensity increases and aggravates the hazard when the voltage is high. The correlation between voltage, current intensity, and resistance is formulated as follows:
Volts = Amperes x Ohms or Amperes = Volts / Ohm
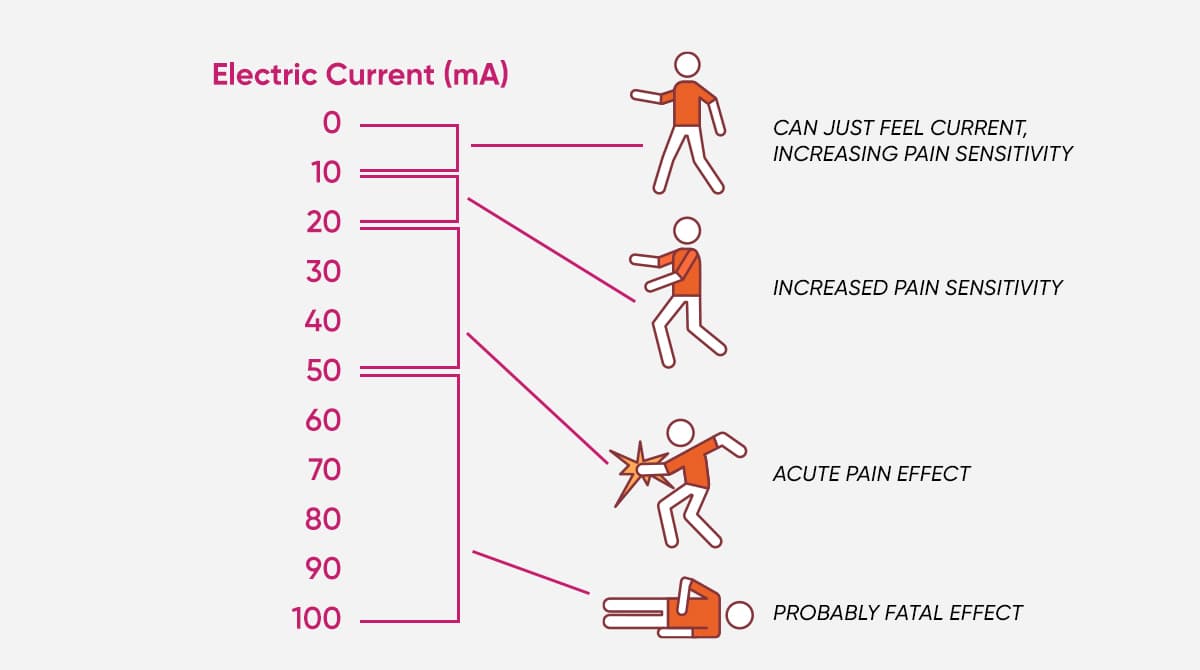
Potential risks based on the current intensity are as follows:
| Current Intensity | Physiological Symptom |
| 0 to 0,1 miliampers | There is the sensation of a tickle in the hand. |
| 1 to 5 miliampers | There is the sensation of pins and needles in the hand. It becomes harder to move hands and arms. |
| 5 to 15 miliampers | At this point, it is possible to release the object being held. Cramps develop in hands and arms. The blood pressure increases. |
| 15 to 25 miliampers | It is not possible to spontaneously release the object being held, but the functioning of the heart remains unaffected. |
| 25 to 80 miliampers | The blood pressure increases. The heart starts to function irregularly. It becomes difficult to breathe in and out. The heart may be arrested, but it is possible to make it functional again. Consciousness remains intact. Some people may faint after 50 mA. |
| 80 to100 miliampers | Heartbeat becomes irregular depending on the duration of the effect. Consciousness is lost. |
| > 3 to 8 ampers | The blood pressure increases. The heart is arrested. Lungs swell. Consciousness is lost. |
-
Resistance Level
The hurdles faced by an electric current on its path are called resistance. The unit of resistance is expressed in Ohm. Current always travels through the path with the least resistance. If the path with the least resistance is the human body, the person is exposed to electric current. Humidity, on the other hand, is a factor that undermines resistance. For example, there is an increased risk of electric shock if a person stands in a puddle. The risk increases even more if there is no contact with water, but the clothes are wet or the humidity is high.
The resistance value is 100,000 Ohms when the human body is dry, while the resistance of a wet body is 1,000 Ohms. So, it is easier for the current to enter the body since humidity reduces the resistance level. Consequently, the person may be exposed to a greater shock.
Points to Consider for Human Health in Electrical Faults
 There are certain actions to be taken to survive electrical faults with minimal damage. All the materials used in installations should comply with TSE standards to avoid potential risks. If power tools are to be used, care should also be taken to keep hands and feet dry. If it is required to work on damp or wet ground, the necessary action should be taken by using a residual current device against ground fault. Additionally, the shoes worn should be insulating.
There are certain actions to be taken to survive electrical faults with minimal damage. All the materials used in installations should comply with TSE standards to avoid potential risks. If power tools are to be used, care should also be taken to keep hands and feet dry. If it is required to work on damp or wet ground, the necessary action should be taken by using a residual current device against ground fault. Additionally, the shoes worn should be insulating.
Before plugging in any electrical devices, one should make sure that the device is switched off. Sockets should be grounded, and sockets with a safety cover should be preferred where available. In case of a fault in the electrical fuse, no wire should be wound around it for repair. In addition, automatic fuses should be used since they would be safer.
Residual current devices should also be used to avoid potential accidents. The operation of residual current devices should be checked once a month. If an electronic device breaks down, it is of great importance to seek the help of people who have specialized in this field. In addition, devices should be used in accordance with their operating manuals.
How to Give First Aid in an Electrical Accident?
The following steps should be followed to give first aid to an electrocuted person:
- The faulty circuit, whom the person having electric current running through their body is exposed to, should be switched off immediately. It is required to remove the plug from the socket, turn on the switch and turn off the fuse. If not possible, the person should be removed from the live place with the help of objects made of insulating materials, such as wood, glass, plastic, mica, paper and rubber.
- An ambulance should be necessarily called. While waiting for the ambulance, it is required to continue performing cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR).
- If the electrocuted person has stopped breathing, they should be given mouth-to-mouth breathing. About 12 breaths per minute should be given. If the heart has stopped beating, it is necessary to start a heart massage.
- If there is a danger such as fire caused by a short circuit, the fire should be extinguished first to ensure safety.
- If the electrocuted person has burns, these parts of the body should be covered with a clean cloth, avoiding the application of any substance.
Have you ever experienced an electrical accident? You can share your views and experiences with us in the comments section.

 Online Services
Online Services Application Inquiry
Application Inquiry Pay Assurance Fee
Pay Assurance Fee Query Installation Number
Query Installation Number Compensation Fee Inquiry
Compensation Fee Inquiry Automatic Payment Order Inquiry
Automatic Payment Order Inquiry Partnership
Partnership






Leave a Comment
Comments (9)
E
Erhan
İsmail bey yorumunuzu gördüm aynısı bendede oldu şuan nasılsınız düzeldinizmi
İSMAİL
Merhaba, 7 Şubat 2024 de Elektrik akımına maruz kaldım. Bir ay oldu. Ben daha önce 220v çarpıldım ama bu kadar uzun şiddetli olmamıştı. Zemin kuru ayağımda spor ayakkabı vardı sigorta kapalı olmasına rağmen kablo bağlantısı yaparken elim sadece kabloya dokundu başka yerle temas olmadı sonra kendimi yere zor attım ellerim ve kollarım uyuştu yerden 20 dk kalkamadım. Birkaç gün sonra sağ baş parmağım ve işaret parmağımda sivilce büyüklüğünde siyahlaştı şu anda yeni yeni geçiyor. Ama on onbeş gündür kalp tarafında ağrı nefes darlığı çekiyorum. Korkmaya başladım kalbime zarar verdi.
A
Ali İhsan
Vallahi azizim biz ilk okul çağındayken, 220voltun üzerimizden geçmesine izin vererek, ampul yakıyorduk, anlatılanların, çoğu deneyimlenmemis,bilim ayağınıza ,toprakla teması kesecek bir şey le alakalı, yâda durduğunuz zemin dilelim çok önemli, bir betona,tahta arısında ki farkla alakalı çarpma etkisi
P
Pınar
Ben 4 gün önce televizyonun fişini çekmeyi unutup televizyonu kapattım sadece islak bezle tv silerlerken aniden vücudumu titreme aldı ve kalp atışı çok hızlı atmaya başladı hemen bıraktım anında sonra hiçbirine sinirlendiğim hissetmiyorum üç gü boyunca toprağa bastım sizce bi hasar kalmış olabilir mi
A
Ayşe
Bana da 3 hafta önce çarptı bir elim kabloda bir elim merdiven demirinde idi. Bırakamadım yapıştım kaldım. Şimdi ara ara kalbime kramp giriyor normal mi acaba. Ve ne kadar devam eder ki
M
Murat
Herkese geçmiş olsun. Allah yardımcısı olsun bütün sıkıntı çekenleri. B1 vitamini kullanmanızı öneririm. Eksikliğinde vücutta sinirler aç kalıyor. B1 eksikliği diye aratıp araçtırmanızı öneririm.
Z
Zeliha çorak
Ben de yıllar önce duş olurken akıma kapıldım. Sakin kaldım vucudum titriyordu bacaklarıma kramp girdi fiskiyeyi tutan parmakları açtım ama fiskiye elimi bırakmadı. Zorla da olsa bir ayağımı kuru alana atınca fiskiye beni bıraktı. Şuan vucudumun sağ tarafı ağrıyor
H
Hüseyin
Beni 2014 yılında ilaçlama yaptım motorda ilaç bitti ilave ilaç yapmak için motorun kollarından tuttum kolun birinde plastik kaplama vardı birinde yoktu plastik olmayan sol bavçumu tuttu uzun süre uğraştım yanmadan ölmeden kurtuldum sayaçtan gelen kaplo ilaç moturunun kaplusu ile birleştiği ekleri yerdeydi suyuda açık unutmuşum bilmeyerek hertaraf elektrik olmuş ilaç motoru beni bu şekilde çarptı ((( şu anki durumum çok hastanelere nöroloji kas ve sinir uzmanı beyin cerhaği na gittim teşsiz koymadılar elektrik çarptı diye anlattım ondan olmaz dediler şu anki durumum kas ve sinirler bitti konuşma bozuldu ayakta duramıyorum iki haşa destekle yürüyorum oturmamda araç kullaňmada sıkıntı yok yüzde seksen engeli oldum böyle olay yaşayan oldumu kas ve sinir tedavisi olurmu bilgilendirenlere tşk ederim not rahatsızlık yavaş yavaş ilerledi
Y
Yiğitcan
Çok kötü, hiç sevmedim 10tane madde nerede