
The most Commonly Used Electrical Terms and Their Meanings
What is in this article?
As in any field/discipline, there are some specific terms used in the field of electricity. By learning about electricity terms and their meanings, you can find out how electricity, which is an important part of everyday life, is generated.
In the rest of our article, you will learn more about the basic concepts of electricity, which is a big part of our daily life, the devices used in measuring electricity, and the most commonly used electrical terms.
What are the Basic Concepts of Electricity?
Commonly used electrical terms:
-
AC
Alternating current is designated by the abbreviation AC. Electricity enters homes as alternating current, and many household appliances such as refrigerators, washing machines, and dishwashers are powered by alternating current.
-
Current
Current: It is generated when electric charges move in a certain direction. It can also be explained as the amount of charge flowing in a circuit in one second. There is a movement from the positive direction of a source to the negative direction. In this context, the direction of electron flow must be opposite to the direction of current flow. When the flow of electric charges changes with time, the value of current also changes.
Current is divided into alternating current and direct current according to the change in direction and intensity over time. The unit for current denoted by the letter I is amperes.
The formula is as follows:
I = Q / t
In this formula, I is the current, Q is the electric charge, and t is the flow time of the charge.
-
Alternating Current
Alternating current is a current whose direction and strength can change regularly as a function of time. For a current to be called alternating current, the transit time and the amount of electric charges must be the same in both directions.
It is generally used in high-power machines and large circuits.
-
Ampere
This unit indicates the strength of the electric current or charge that flows through the device per unit time. It is denoted by the letter A. In electrical circuits, units of kiloamperes and amperes, equal to 1,000 times the ampere, are commonly used.
However, in electronic circuits, smaller units such as microamperes (one millionth of an ampere) and milliamperes (one thousandth of an ampere) are also used. Amps are calculated by dividing the electric charge by the unit of time. 1 ampere flows through a 220-watt circuit. The voltage value of this circuit is 220 volts.
-
Ammeter
An instrument used to measure the amount of current flowing through the circuit. For measurement, the instrument must be connected in series with the current flowing in the circuit.
For ammeters with a very small internal resistance between 0-1 Ω, coils with few windings (number of winding of coil wires) and thick coils are used. If the instrument resistance is large, the total resistance in the circuit increases and the circuit does not work.
The parallel connection of the ammeter with small internal resistance to the circuit causes a short circuit. The circuit is damaged or blown because a high current flows through it that the instrument cannot handle.
-
Switch (Circuit Breaker)
A switch is a circuit mechanism that allows or prevents the passage of electric current in an electrical circuit. It is used to open and close the circuit.
-
Avometer
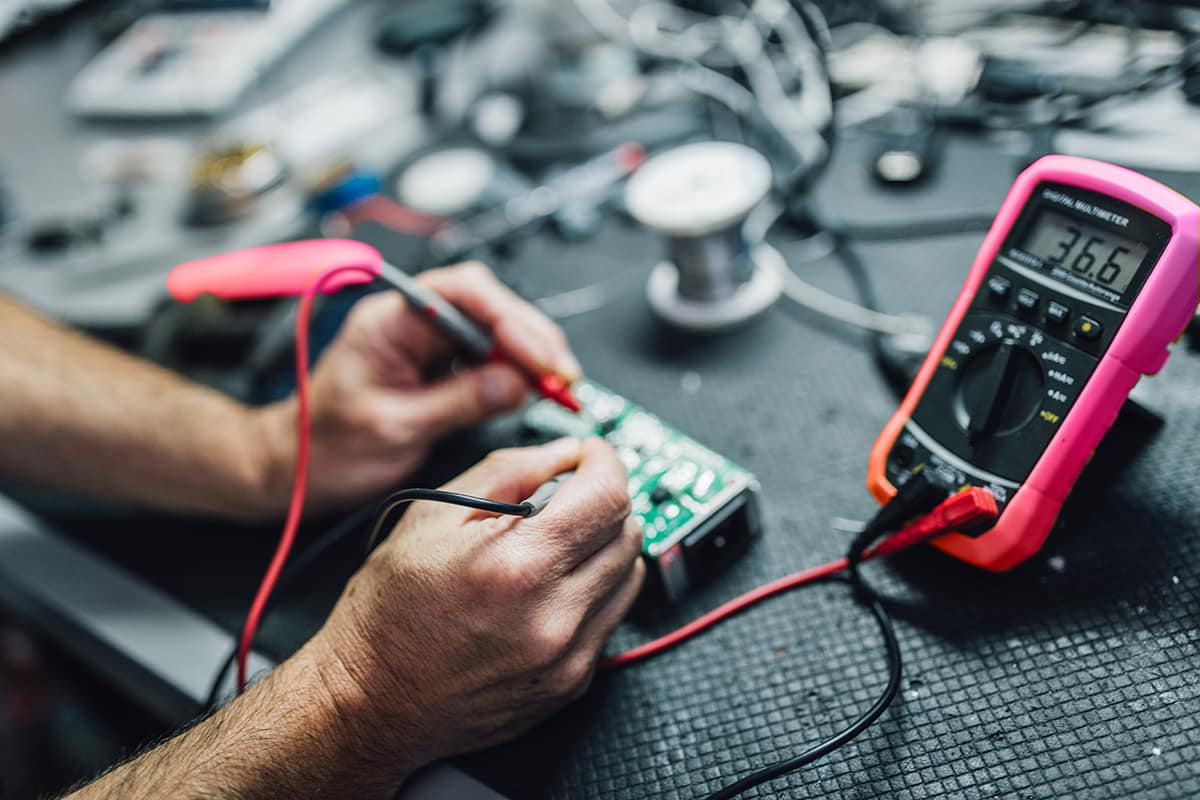 Avometer is an instrument for measuring resistance, current and voltage in an electrical system. The name of the instrument comes from the initials of the terms ampere, volt and Ohm. It is also called multimeter because it is suitable for multipurpose use.
Avometer is an instrument for measuring resistance, current and voltage in an electrical system. The name of the instrument comes from the initials of the terms ampere, volt and Ohm. It is also called multimeter because it is suitable for multipurpose use.
The settings selected for direct current, alternating current and resistance measurements with avometers vary. Instruments connected in series to the circuit during current measurement are connected in parallel during voltage measurement. In resistance measurement, the avometer is attached to both ends of the electrical circuit.
Avometers are divided into two, digital and analog. Analog avometers have a single scale for measurement and reading operations.
Digital avometers, on the other hand, have LCD screens, making it easier to read the measurements. In order to make measurements with these instruments, probe connections must be selected in accordance with parameters such as commutator stage and size.
Although the features and usage of these two instruments are different, the measurement is carried out in the same way.
-
Coil
A circuit mechanism formed by spirally winding conductive electrical wires into a material called a core. The wires may be wound on top of each other or side by side. Winding refers to each winding of these wires. There are different types of coils such as iron core, air core and tuned coils.
When alternating current is applied to the coil, the resistance of the current changes. The unit of this resistance, called inductance, is Henry and its symbol is H. The type of core on which the wires are wound, the number of strands and the cross-section of the coil are the values that are taken into account when determining the inductance.
-
DC
Direct current; it is designated by the abbreviation DC. It is used in electrical circuits because its direction and intensity do not change with time. Batteries are the direct current source used in households.
-
Dynamic Electricity
Dynamic or mobile electricity is the flow of electrons between two bodies with different charges.
-
Resistance
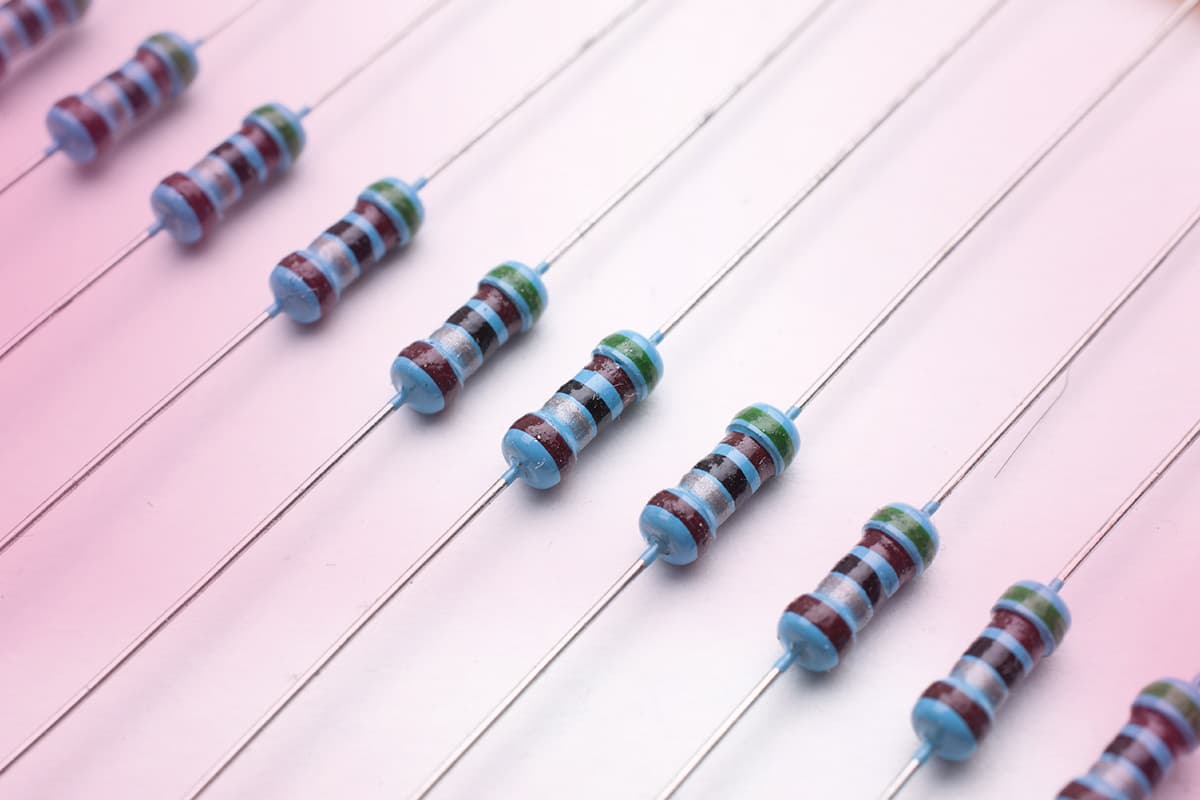 Resistance is the resistance to electric current when any power is applied. Resistance, whose unit is ohms, is denoted by the letter R. It can be connected to a circuit either in series or in parallel or mixed. The parallel and the series connection of a resistor in a circuit is called a mixed circuit.
Resistance is the resistance to electric current when any power is applied. Resistance, whose unit is ohms, is denoted by the letter R. It can be connected to a circuit either in series or in parallel or mixed. The parallel and the series connection of a resistor in a circuit is called a mixed circuit.
It is divided into different types, such as fixed and average effective resistance. Fixed resistors, whose value does not change, have high sensitivity. In case of adjustable resistor, it is possible to adjust the resistance value manually.
Ambient effective resistance: It is influenced by environmental factors such as heat and light in the vicinity of the circuit. Therefore, the value of the resistance may vary.
Related Article

What is Ohm? Discover the Unit of Ohm
-
Direct Current
It is a current whose direction does not change with time, but whose intensity can change. It is divided into two, smooth direct current and variable direct current depending on its intensity. Smooth direct current is a type of current in which the direction or intensity does not change over time. Variable direct current is a current whose intensity changes over time, while its direction does not change.
-
Lamp Socket
Lamp socket; It is an electrical circuit element that allows the light bulb to be fixed in a circuit and has a grooved slot.
-
Electrical Potential
Potential is the electrical charge of any point or end in an electric circuit. Any electrically charged object has some potential. These objects exert an electric field on their surroundings that corresponds to their electric potential.
-
Electric Charge
When an object approaches an electrically charged object, it is affected by the force released. {This effect is called electric charge and it can be negative (-) or positive (+). The electric charge, in units of Coulomb, is denoted by the letter Q. Coulomb, the unit of charge, is denoted by the letter C. If there are 624x1016 electrons or protons, an electric charge of 1 °C can occur in an object in an object that has no electric charge but contains positive and negative particles, the positive and negative particles are in equilibrium. If there is a lack of electrons in this object, it is positively charged; if there is an excess of electrons, the object is negatively charged. The repulsion or attraction of electric charges is explained by Coulomb's law.
-
Phase
In alternating current, in addition to the uncharged terminals, also known as the neutral, there is another terminal through which the current flows. This terminal is called the phase. Unlike direct current, there are no positive and negative terminals on these devices. The single-phase 220 V alternating current used in households is called single-phase. High-voltage current, called three-phase current, is used in stores and industrial facilities.
-
Voltage
The potential difference between the receiving terminals in a closed circuit, which allows the passage of electric charge between these terminals, is called voltage. It is obtained from electrical energy sources such as alternator, battery, dynamo or accumulator. Voltage, which comes in alternating and direct current varieties and whose unit is volts, is denoted by the letter U.
The voltage can be different at each point of an electric circuit. When a point in the circuit approaches the load, the voltage increases, while when it moves away, the voltage decreases. In this sense, the potential difference is higher at the ends near the load.
-
Conductor
Objects containing atoms with 3 or fewer electrons in the last orbit are called conductors. Conductivity is the opposite of resistance and simply means that something is being transported or passed through.
The formula for conductivity, whose unit is Siemens, is as follows:
1 / R
According to this formula, the conductivity of an object with a resistance of 1 ohm is 1 S.
-
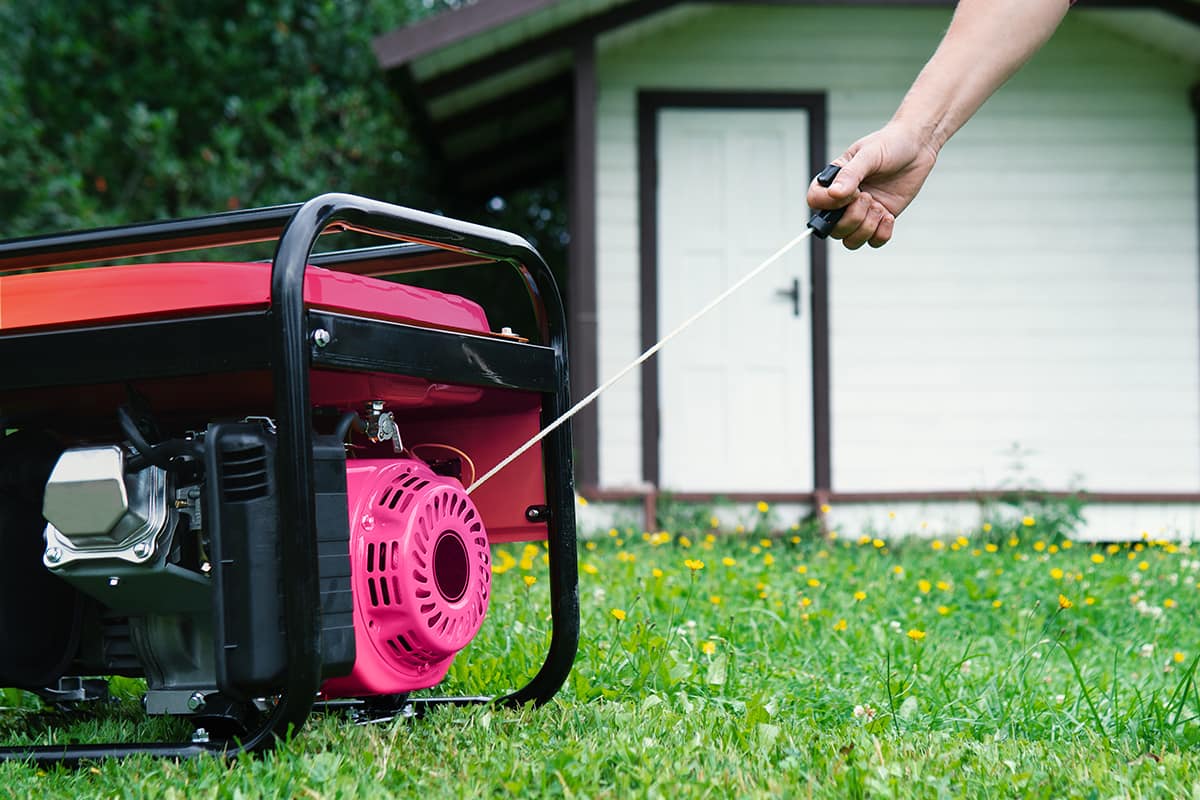
Generator
A generator is an electromechanical device that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy. It is used to generate electricity in the event of a power failure. The first generator was found in an experiment by Faraday in 1831.
For more detailed information about generators, you can examine our article titled What is a Generator? Working Logic of Generators and Power Generation.

-
Leakage Current (Electricity Losses)
Leakage current is the current that is transmitted to the ground as a result of contact of a conductive object having voltage with another object if the insulation is not properly insulated. Whether there is an electrical leak in your sockets can be determined by touching the socket with a pen.
-
Short Circuit
The contact of two points with different voltages in a circuit causes a short circuit. As a result of a short circuit, a new circuit is created with a low impedance value (resistance of the circuit to current). This means that a high amount of current flows from the points where current flows to the points where there is a short circuit. There is a three phase short circuit, two phase ground short circuit, and a single phase ground short circuit etc.
-
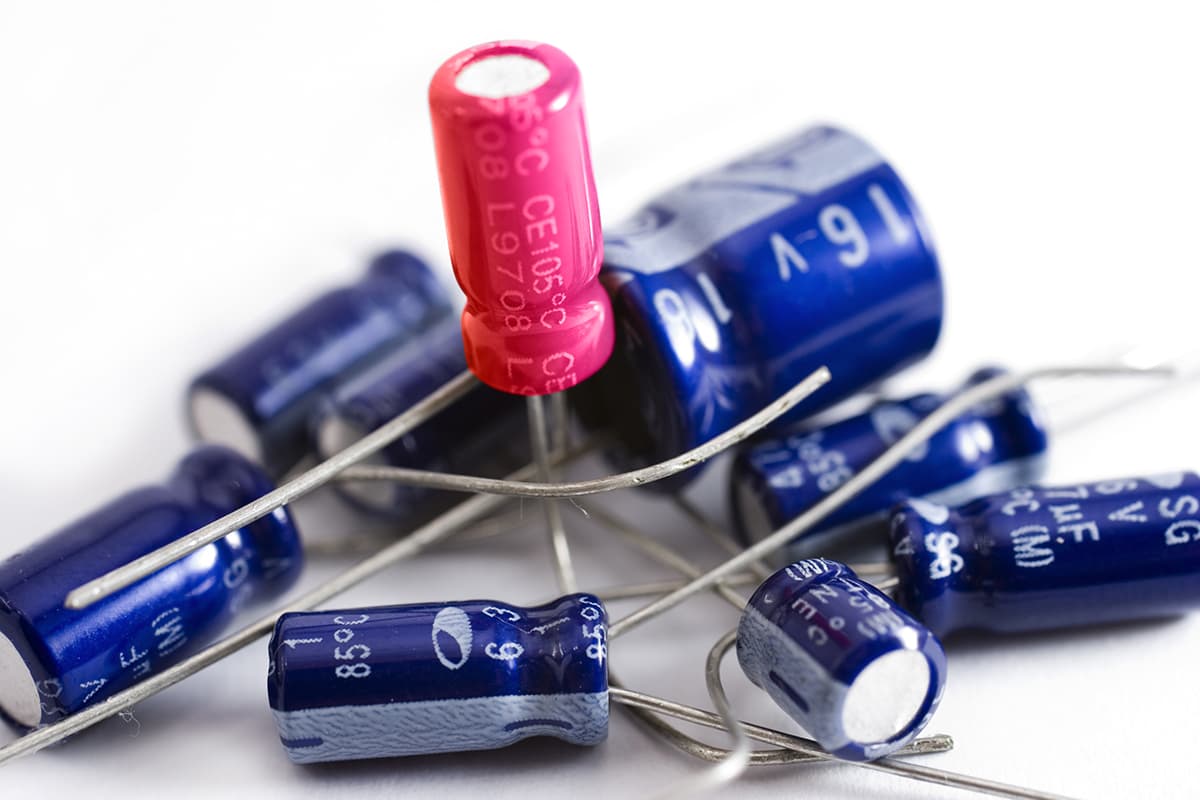
Condenser or Capacitor
Condenser or capacitor is one of the electrical circuit elements formed by placing an insulating object between metal layers. It is used to store electrical energy. Capacitors utilize the polarization of electrons, which allows the electrical charge to be stored.

-
Contactor
Contactors are powerful electromagnetic switches that can be remotely controlled to open and close electrical circuits. A contactor consists of a paddle, electromagnet and contacts.
-
Ohm
Ohm, the unit of resistance, is denoted by the symbol Ω. The higher multiples of this unit are megaohm (MΩ) and kiloohm (KΩ).
-
Ohmmeter
An instrument for measuring the resistance of an electrical circuit is called an ohmmeter. An ohmmeter consists of an ammeter, a resistor and a battery as an energy source. Some instruments also include a push button for operation. The alternating current source inside the instrument allows the ohmmeter to measure without any power source.
However, it is not possible for the ohmmeter to work without a battery or any source other than a battery. In order for the instrument to make a measurement, the energy in the electrical circuit must be cut off.
-
Lightning Rod (Lightning Arrester)
Lightning rod is a device used to protect buildings from the destructive effects of lightning such as light, heat, pressure, sound, electromagnetic. One end of the lightning rod is located on the building and the other end is buried in the ground. Lightning striking the lightning rod at the highest peak of the building is transmitted directly to the ground.
You can also examine our article What Is a Lightning Rod? How Does It Work? Vitality of a Lightning Rod to read about the importance and functioning principle of lightning rods in detail.

-
Relay
Relay; It is an electrical circuit element used to operate a high-power receiver with a low value current. There are different types of it, such as single contact, 5 contact, 10 contact. It consists of contact, coil, pallet, core and spring parts.
-
Fuse
Fuse; It is a circuit element used to protect active lines and electrical circuits through which electric current flows. Thanks to the fuse, situations such as short circuit or overload on the lines are prevented. At the same time, users are also protected against electric shock.
The fuse, which is connected in series to the circuits, ensures that the electrical circuit is opened in case of high current flow. Bladed, automatic, glass, bushing fuses and high voltage fuses are types of fuse used in different areas
-
Static Electricity
Static electricity, also called static or non-moving electricity, refers to the electricity generated by static charges. Although it is not possible to talk about any movement or flow, objects with static electric charge can repel or attract oppositely charged objects. Static electricity is generated by the contact or friction of two conductive or insulating materials with each other.
-
Grounding
Grounding is the integration of the non-voltage metal parts of an object into the ground with the help of a conductive material. The purpose of grounding is to ensure that living beings using circuits through which electric current passes in cases such as overload are less damaged and that the circuit continues to function.
You can find all the information about grounding in our article titled What is Electrical Grounding?
-
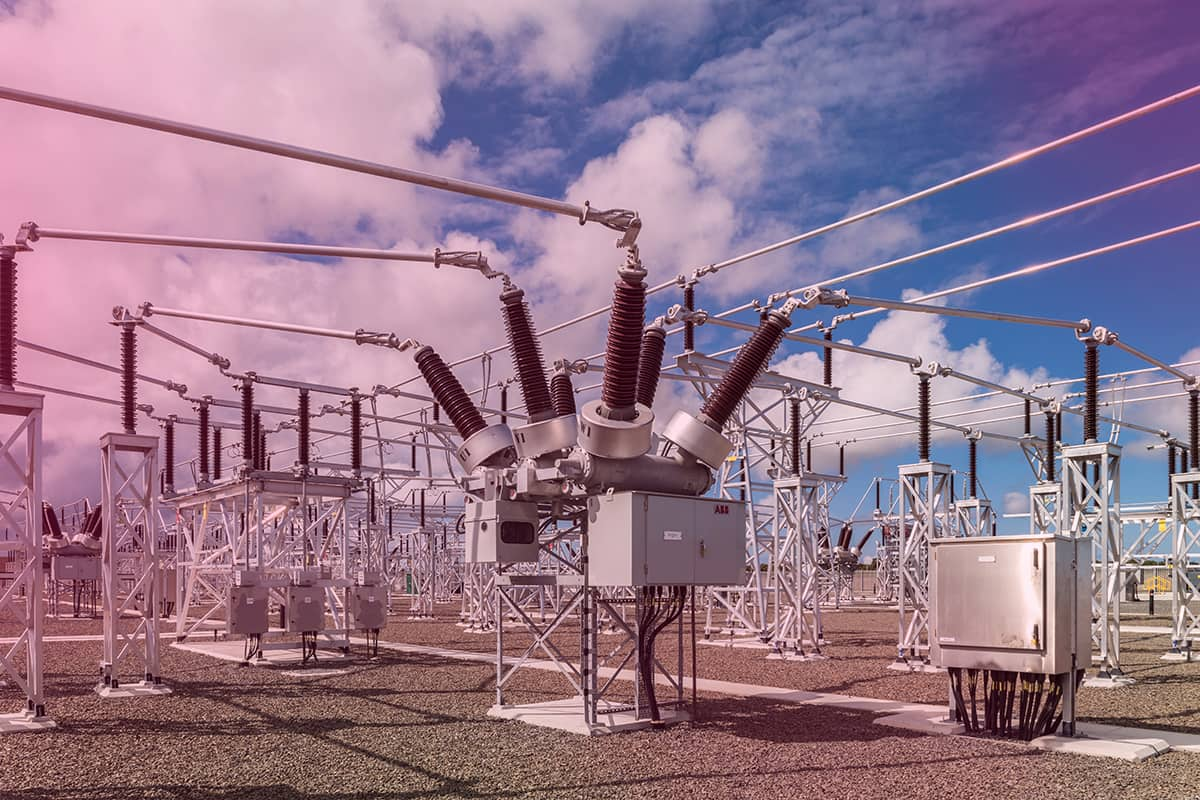
Transformer
Transformers, provide energy flow between circuits with the help of electromagnetics. They can raise or lower current and voltage values. Transformers are used to prevent voltage drops and power loss in power lines. It helps to reduce electricity losses by keeping the power constant.

-
Volt
Volt is a unit of voltage, also called potential difference. It is represented by the letter V. In a circuit with a current of 1 A and a resistance of 1 Ohm, the voltage is 1 V.
Related Article

What is Volt? What is the Volt Unit?
-
Voltmeter
Voltmeter is used to measure the potential difference or voltage in an electrical circuit. In an electrical circuit, the potential difference between the receivers is measured with a voltmeter, denoted by V. Voltmeters with high internal resistance are connected parallel to the circuit. A short circuit may occur due to the small internal resistance. In order to increase the resistance, care is taken to ensure that the coils in these instruments are wound and feature thin-wires.
When the voltmeter, which should be connected in parallel, is connected in series, the resistance increases significantly. This causes the current not to pass through the circuit or to pass very little causing the circuit not to work.
-
Watt
The unit of power, the Watt, is denoted by the letter W. In a circuit with a current of 1 A and a voltage of 1 V, the power is 1 W. The formula is as follows:
Power (Watt) = Current (Ampere) x Voltage (Volt)
Related Article

What is Watt? How to Calculate with Watt Formula?
-
Insulator
Substances that do not conduct electric current because the electric charge cannot flow freely are called insulators. Objects containing atoms with 5 or fewer electrons in the final orbit are insulators. In order to increase insulation, the amount of electrons in the last orbit of atoms must increase. These objects are used to prevent electricity leakage and current from harming living things.
You can learn more about electricity in our blog. Which of the electricity terms did you read for the first time in this article? We are waiting for your comments.

 Online Services
Online Services Application Inquiry
Application Inquiry Pay Assurance Fee
Pay Assurance Fee Query Installation Number
Query Installation Number Compensation Fee Inquiry
Compensation Fee Inquiry Automatic Payment Order Inquiry
Automatic Payment Order Inquiry Partnership
Partnership





Leave a Comment
Comments (1)
s
sertan Tokdemir
Gerilim ve sigorta yazıları okudum güzel makaleler bilgiler
Aydem Perakende
Merhaba, İlginiz için teşekkür eder, keyifli okumalar dileriz 😊