
Who is Alan Turing, the Pioneer of Computer Science
What is in this article?
If you have an interest in science and technology, you’ve probably heard of Alan Turing. Alan Turing is the founder of computer science, a mathematician and a cryptograph among many other titles, and his ideas about computers and the artificial intelligence technology are the basis for the technology we have today. Alan Turing proved he was one of the unmatched geniuses as a child, and later on, he carried out successful studies in numerous fields in a lifetime of 41 years. In addition to his work on cryptography, which changed the fate of World War II, the Turing test is also considered one of the major criteria as it is still used today to measure the level of development of artificial intelligences. Let’s find out who Alan Turing was and take a closer look at his life and work.
 Short But Successful Life of Alan Turing
Short But Successful Life of Alan Turing
Alan Turing lived from 23 June 1912 to 7 June 1954, and his studies throughout this lifetime made him one of the pioneers in numerous fields, in particular computer science. Born into an upper-middle class family in London, Turing had problems adapting to school during the early years of his education. The signs of genius he showed and his interest in science greatly affected his subsequent years. Although he is famous for his work on computer sciences and cryptography, he also had an interest in quantum mechanics, physics and biology.
Alan Turing started Kings College in 1931 and once he completed his education, he published an article on the Turing machine. In 1938, he went to the Princeton University for a Ph. D. in mathematics. Turing also took lessons on cryptography here, and upon his return to England, he worked on resolving the encrypted messages from enemies at the Bletchley Park, which was the center of communication for the English government during the war. After the war, he focused on ACE and artificial intelligence, which are the bases for the computer we have today.
His Contributions to Mathematics and Computer Science
Alan Turing is mostly known as a mathematician and is known for his contributions to mathematics. Alan Turing’s studies on mathematics crossed paths with computer science when he designed the universal Turing machine. As he was looking for a solution to something known as entscheidungsproblem or the decision problem, he came up with the hypothetical idea of the Turing machine in 1936. This problem asks if an algorithm can exist that returns a yes or no answer to a question that is about an expression that is input and if it is universally valid or not.
Alonzo Church and Alan Turing, in the same period of time, used different methods to reveal that there are mathematical problems that cannot be resolved by an algorithm. Known as the Church-Turing thesis, this study states that the computational power has a limit to it. In the following years, Alan Turing did his Ph. D. with Alonzo Church at the Princeton University.
The Hero of World War II
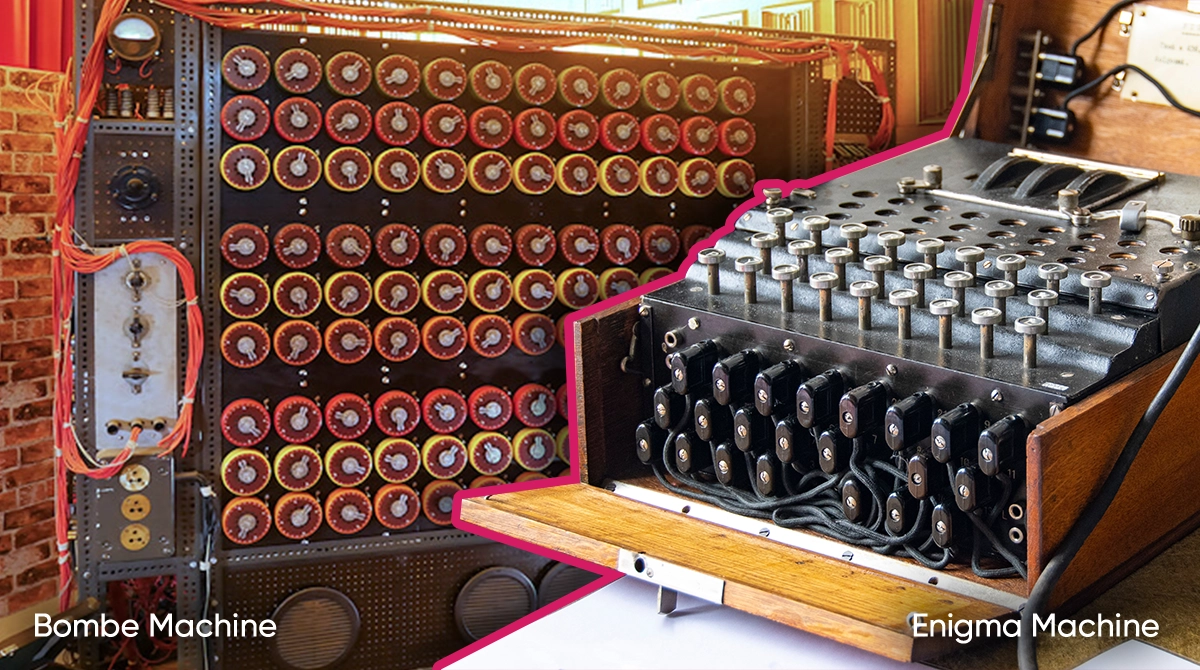
Alan Turing’s studies played an important role in the victory of the Allies in World War II . Designed by Germans and used for encrypted communication, the Enigma was actively used before and after World War II. The Enigma was one of the most powerful devices designed to that date for encrypted communication. In the early 1930s, Polish scientists and cryptographs, led by Marian Rejewski, managed to read the messages created with the Enigma. However, when the Germans made the Enigma even more powerful during World War II and started to change the encryption system on a daily basis, it became almost impossible to decipher the messages using the then-current system.
It took a short time to listen to the messages transmitted with the typewriter-like Enigma, which was used to send encrypted messages; however, it was considered impossible to crack these messages as there were 159 billion possible encryptions. A group of cryptographs led by Alan Turing started to work at the Bletchley Park to resolve the Enigma encryption, based on the previous work of their Polish colleagues. To resolve the encryption of the Enigma, Alan Turing started to work on the Bombe, which was a rotor device simulating Enigma’s mixer. The Bombe was capable of resolving the Enigma’s encryption much faster than a human could. Designed in 1940, the Bombe allowed for intelligence that changed the fate of the war. In 1942, 39,000 encrypted messages a month were being resolved at the Bletchley Park. In the subsequent phases of the war, this number was raised to two per minute, which equaled 84,000 messages. This successful work by Turing during the wat brought him “The Most Excellent Order of the British Empire”.

The Turing Test and Artificial Intelligence
The studies Turing carried out during the war made him even more interested in the computer science. He started to work on the Automatic Computing Engine (ACE) at the National Physical Laboratory in London. Unfortunately, his designed could not be built as planned for various reasons. When his first functional electronically-stored program computer was defeated by the scientists at the Manchester University, Turing got discouraged but he kept on working. In 1948, he started to work on the Mark I for the Manchester University. He created the very first programming system and guide.
One of the most impressive pieces of work by Turing is the Turing Test, which made him one of the pioneers in artificial intelligence. Alan Turing started his work on artificial intelligence with the idea that the human brain is a digital computing machine. The human brain was an unadjusted machine right after birth but in time, it became a functional machine through education. Turing’s ideas on the human brain and computers subsequently led him to question if computers could think just like humans. In 1950, he developed the Turing Test, which is a commonly used criterion to determine if a computer is actually capable of thinking.
In the Turing test, a human interrogator must ask various questions to the computer and according to the answers from the computer, determine if they are interviewing with a questioning human being or with a computer. In short, the artificial intelligence must convince the interrogator that it is a human being. Today, artificial intelligence applications are made public with ChatGPT, which made the Turing test popular again. However, although there are applications that pass the Turing test, we have not yet reached the artificial intelligence technology that can think like a human being.
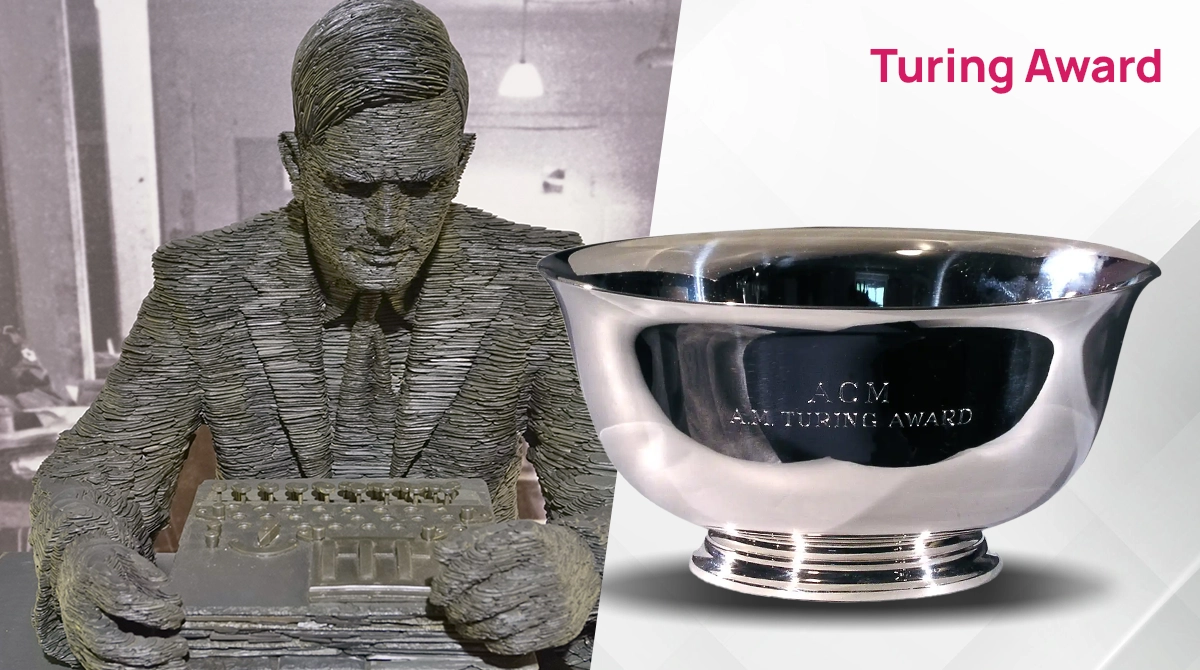 The Turing Award and Events Named After Alan Turing
The Turing Award and Events Named After Alan Turing
Discussions regarding the cause of death of Alan Turing are still going on after all these years. Although official records state that Turing took his own like, some claim that he was murdered. No matter what caused his death, Alan Turing is duly respected today as one of the pioneers in computer science and artificial intelligence.
The Association for Computing Machinery (ACM) has granted the Turing Award since 1966, which is considered the Nobel Prize of the computing world. Today, there are numerous information signs in many regions of England regarding the life of Alan Turing. There is also a statue of him at the Bletchley Park. Various events are held around the world to honor Alan Turing’s memory.
Take a look at our other content about scientists who shaped the future with their studies and about the most interesting subjects of the science world like the dark matter.

 Online Services
Online Services Application Inquiry
Application Inquiry Pay Assurance Fee
Pay Assurance Fee Query Installation Number
Query Installation Number Compensation Fee Inquiry
Compensation Fee Inquiry Automatic Payment Order Inquiry
Automatic Payment Order Inquiry Partnership
Partnership







Leave a Comment