
What Is SF6? Where is the SF6 Circuit Breaker Used?
What is in this article?
SF6, known for its exceptional arc-extinguishing and insulation properties, is a go-to choice for electrical distribution and transmission systems. While SF6 is categorized as a greenhouse gas, it's important to mention that it poses no direct threat to human health.
So what is SF6 gas and what are its properties? Let's take a look at the details about SF6 gas together.
What is SF6 Gas? What Are Its Properties?
Sulfur hexafluoride (SF6) is a greenhouse gas that's colorless and odorless. It is formed from the combination of sulfur and fluorine atoms. This gas is electronegative, meaning it has a high affinity to attract electrons. It's also non-flammable, making it a preferred choice in preventing explosions, particularly in electrical systems. What sets SF6 apart is its insulating properties.
At a molecular level, the structure of SF6 is defined by a central sulfur element surrounded by six fluorine atoms. This unique configuration ensures both electrical and chemical stability, making the gas exceptionally reliable. SF6 is identified as a non-polar gas and is classified as a hypervalent molecule, with eight additional electrons in its outermost orbital.
Although its solubility in water is limited, SF6 is typically transported in a liquefied form. Given its density, which is greater than that of air, SF6 is extensively used in the electricity and energy industry. The properties of SF6 can be outlined as follows:
- High arc extinguishing performance. Electrical explosions caused by low resistance connections in an electrical system are termed arcs. SF6 effectively prevents these types of electrical explosions due to its superior electrical insulation.
- Despite its excellent electrical insulation, the gas also conducts heat.
- Its dielectric resistance makes the gas especially standout,
- Notably higher than air, being more than 2.5 times greater.
- It is a non-toxic gas, and thus doesn't pose any direct threat to human health.
In the industrial sector, it serves as a protective agent during castings. In the glass industry, it is used for sound insulation. Within the medical domain, it finds application in ultrasonic tests for diagnosing ear and eye ailments.
It is also utilized as a feeder material in plasmas. It is also widely used in vehicle tires, semiconductor manufacturing, the production of electron microscopes, military radar and aircraft equipment, particle accelerators, the automotive sector, in tennis balls, as well as in metallurgy, meteorology, and X-ray equipment.
Due to its high arc quenching capability, SF6 is preferred in the electricity and power industries. Due to its high electronegativity, the gas absorbs the free electrons caused by the arc between the contact and the circuit breaker. SF6 gas has a unique property that allows it to create a cooling effect in circuits and systems. Due to this cooling capability, it is frequently utilized in the production of circuit breakers.
Why is the SF6 Gas Preferred as a Circuit Breaker?
In 1900, the first production of SF6 gas took place at the Faculte de Pharmacie de laboratory. By 1937, the General Electrical Company recognized that SF6 gas had potential as an insulating material. During the second half of the 20th century, particularly after World War II, the adoption of gas for insulation in electrical systems witnessed a significant surge.
Indeed, the demand for gas in commercial applications grew, and its production became popular on a global scale. In 1948, the first commercial production of SF6 gas was undertaken by Allied Chemical Corporation, Pennsalt in the USA.
The adoption of SF6 gas in high voltage switchgear became prevalent during the 1960s. Its potential in electrical systems led to a surge in demand across Europe and America. Recognizing its exceptional arc extinguishing capabilities in terms of electrical properties, the gas soon found its application in circuit breakers.
The first SF6 insulated substation in the world was established in 1966 in Paris. By 1971, circuit breakers made with sulfur hexafluoride had entered the market. The material's prominence as a circuit breaker is attributed to its high electronegativity, dielectric strength, and remarkable arc extinguishing potential.
-
Is SF6 Necessary?
SF6 gas and vacuum are used as a cutting technique with electric shaft devices. While the vacuum is seen as a more advanced arc quenching method compared to SF6 gas, due to its distinct technical properties, SF6 gas remains the sole technique viable for cutting and insulating in high and medium voltage systems up to 800 kV.
In addition, the material allows the production of small size devices at lower cost. Consequently, SF6 gas is indispensable in electrical equipment for its role as an arc extinguishing technology.
Related Article

What Is Electricity Fuse? How Does It Work? Why Does It Blow?
How Does an SF6 Gas Circuit Breaker Work?
To prevent electrical explosions, SF6 gas is used in the manufacture of circuit breakers. Depending on the environment in which the extinguishing operations are carried out, the circuit breakers feature different designs. SF6 gas circuit breakers are high-performance devices known for their effective extinguishing of electrical explosions.
The working principle of the SF6 gas circuit breaker, predominantly used indoors, hinges on the compression of sulfur hexafluoride by the moving piston, which then forces it onto the arc in the contact.
With the insulating properties of sulfur hexafluoride, SF6 at a pressure of 1.5-6 bar reduces the opening distance between contacts. Thus, the arc cools down under the influence of SF6 and the electrical conductivity between the contacts disappears. The damping process for the explosion takes place, and insulation in the contact occurs.
Meanwhile, the fluorine ions in the structure of the gas, thanks to their electronegative property, capture electrons in the environment. Consequently, the reaction within the substance's structure aids in limiting the explosion current. The SF6 gas breaker ensures rapid removal of heat in the environment. The device also reduces the temperature at high speed and helps to prevent explosions in electrical equipment.
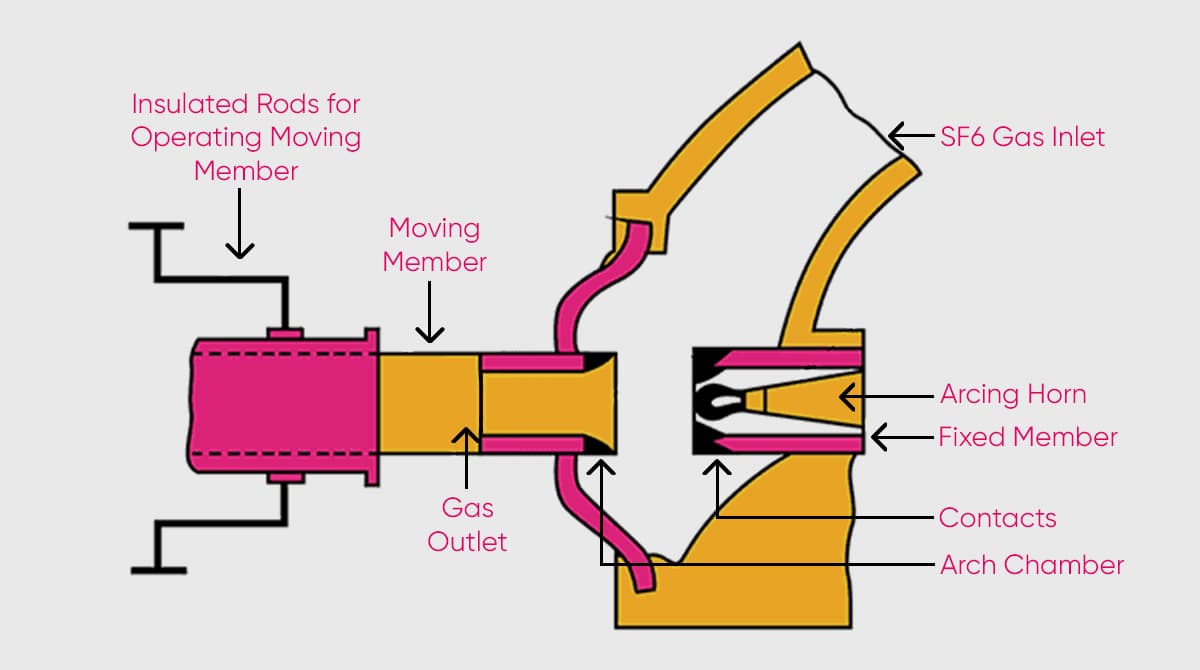
Types of SF6 Circuit Breakers
A circuit breaker is a device, akin to a surge arrester, designed to shield electrical systems from short circuits, fault currents, or overloads. Modern electrical systems employ a mechanism constructed by integrating various devices.
Circuit breakers play a crucial role in safeguarding electrical systems from issues like cable faults, excessive current, and short circuits. Various types of these devices can be found in the market, including vacuum, air blown, oil operated, SF6 gas, and pneumatic. Among these, the SF6 circuit breaker types incorporate sulfur hexafluoride gas in their manufacturing process.
There are three distinct types of SF6 circuit breakers available. These product types include the double beam piston, non-inflating piston, and the single beam piston SF6 circuit breaker.
-
Double Beam Piston SF6 Circuit Breaker
The double beam piston SF6 circuit breaker utilizes sulfur hexafluoride gas compressed in a cylinder to quench electrical arcs. During the arc extinguishing process, the gas transitions from a high-pressure state to a low-pressure state. However, the usage scope of this product is somewhat restricted when compared to other types.
-
Single Beam Piston SF6 Circuit Breaker
The single beam piston SF6 circuit breaker is crafted with a hollow cylinder. This cylinder serves as a bridge between two contacts. The piston, integrated with the cylinder, moves between the two fixed contacts and is employed to either establish or disrupt the contact. Typically, the product is suitable for use in the voltage range of 13.6- 760 kV.
-
Non-Inflating Piston SF6 Circuit Breaker
The non-inflating piston SF6 circuit breaker represents the initial model that was manufactured. Its operational principle can be likened to that of an air-blown circuit breaker. However, with the introduction of newer varieties of SF6 circuit breakers, the application scope of this product has diminished.
SF6 Circuit Breaker Scope of Use
SF6 circuit breakers are typically employed to safeguard electrical equipment from high voltages, like lightning rods. They are very effective devices for extinguishing arcs caused by faults in the system.
SF6 circuit breaker scope of use:
- Electrical transformers
- Electrical distribution and control systems
- Electricity generation plants
- Electricity networks
- Wires in electric circuits
- Capacitor circuits

Advantages and Disadvantages of the SF6 Circuit Breaker
As with any device, it can be said that the SF6 circuit breaker has advantages and disadvantages. The advantages of the SF6 circuit breaker can be listed as follows:
- It is a device with high mechanical strength. It can perform 20 opening and closing operations at short-circuit current and 10,000 opening and closing operations at main current.
- Changes in atmospheric conditions do not affect the performance of the circuit breaker.
- The device is small and easy to maintain.
- It has high arc quenching performance.
- The material used in the device has no explosive properties and does not pose an explosion and fire hazard in electrical installations.
- The heat conduction coefficient of the device is quite high, so the arc can cool down quickly. It quickly dissipates the heat to the environment.
- The circuit breaker is easy to operate, the risk of accident is low. It is possible to have the equipment switched off again.
- It has more effective arc quenching performance compared to air circuit breakers.
- The device has a compact structure.
- The dielectric strength of the device is high. This makes it suitable for high current interruption.
- It has the function of managing all kinds of switching operations
- The equipment has a service life of more than 30 years, making it ideal for long-term use.
- It does not react with minerals.
The disadvantages of SF6 circuit breakers are as follows:
- Additional equipment is required to renew or replace the SF6 gas in the device.
- Such circuits must be monitored and kept under control in the event of a gas leak.
- This equipment can be costly compared to its counterparts.
- The sulfur hexafluoride gas in the device easily causes liquefaction problems at low temperatures and pressures
- The internal parts of the device require regular maintenance.
-
Is the SF6 Gas Harmful to Health?
One of the greenhouse gases in the atmosphere is known as SF6. Although the gas is not harmful to health and has no toxic effects on humans and other living things, it has some effects on the environment and climate due to the fact that it is a greenhouse gas.
In fact, SF6 gas is also used in certain medical treatments. SF6 gas is preferred in ultrasound tests to diagnose ear and eye diseases. However, since the SF6 gas is substance, inhalation is not recommended.
Because it is a heavier gas than oxygen, it can be difficult to remove from the lungs. While the human voice thins when helium gas is inhaled, inhaling SF6 gas causes the voice to thicken.
-
Kyoto Protocol and Greenhouse Effect of SF6 Gas
The use of SF6 gas has been restricted due to its contribution to the greenhouse effect and its impact on the climate.
 The global warming effect of sulfur hexafluoride gas is 23.500 times higher than that of carbon dioxide. In terms of environmental impact, the substance causes a global temperature increase in the atmosphere. However, since it does not contain chlorine in its chemical structure, it does not cause ozone depletion.
The global warming effect of sulfur hexafluoride gas is 23.500 times higher than that of carbon dioxide. In terms of environmental impact, the substance causes a global temperature increase in the atmosphere. However, since it does not contain chlorine in its chemical structure, it does not cause ozone depletion.
The impact of SF6 gas on global warming is estimated at 0.1%. Because it is recognized as a potent greenhouse gas, it is one of the six gases monitored under the Kyoto Protocol, as its impact on the environment in the event of leakage is very large.
The Kyoto Protocol, adopted in 1992 at the Rio de Janeiro Summit, is an international treaty.
The goal of the protocol, called the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change, is to reduce and stabilize the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, which is associated with risks to the climate.
Therefore, the annual release of SF6 emissions in high-voltage facilities should be only 0.5%. To avoid gas emissions, sulfur hexafluoride should be used only in closed systems.
-
Does the SF6 Gas Damage the Circuit or Equipment?
Since SF6 belongs to the group of inert gases, it does not react with metals and does not damage the equipment. If the gas is contaminated with water, it can have a corrosive effect on by-products.
If it leaks into equipment, it can cause permanent damage to main contacts, arcing contacts, insulators and shields. Therefore, gas leaks should be monitored.
So what do you think about the SF6 gas? Is SF6 a harmful gas to the environment or should it be widely used due to its strong effect in arc absorption? Feel free to share with us your thoughts on sulfur hexafluoride.

 Online Services
Online Services Application Inquiry
Application Inquiry Pay Assurance Fee
Pay Assurance Fee Query Installation Number
Query Installation Number Compensation Fee Inquiry
Compensation Fee Inquiry Automatic Payment Order Inquiry
Automatic Payment Order Inquiry Partnership
Partnership





Leave a Comment