
Types & Characteristics of Utility Poles and High-Voltage Poles
What is in this article?
Electric power is an indispensable part of modern life and its transmission to remote places, once it is generated, is just as important.
In the early years of electrical energy, there was no need for very high levels of power because the places generating and consuming energy were close to each other, but nowadays, with the increase in demand, it has become necessary to transmit electrical energy to cities and industrial areas that are further away from the places where the energy sources are located. Meanwhile, losses in transmission highlighted the need for solid utility poles along with the conductor diameters and quality.
You will find a lot of interesting information in our blog, including the characteristics and types of utility poles used in transmission of power, and whether birds landing on power lines get electrocuted.
Why Do We Need Utility Poles? Why Are They So Important?
Utility poles serve to transmit electrical power. Poles are usually used to carry high voltage cables and these cables need to be supported, being tall and robust structures capable of carrying high-voltage cables.
Playing an important role in the distribution of electrical energy, utility poles are also needed to install transformers that supply electricity to certain parts of the power grid and other equipment. Utility poles can also be used for street lighting, traffic lights, communication lines and other infrastructure systems.
They play an important role in people's daily lives. Without them, many modern devices cannot function, which would mean a significant compromise on the comforts of modern life. Utility poles are also important in disaster situations. Earthquakes, storms, floods and other natural disasters can damage these poles, and until they are repaired, there is sadly no alternative method for distributing electrical power.
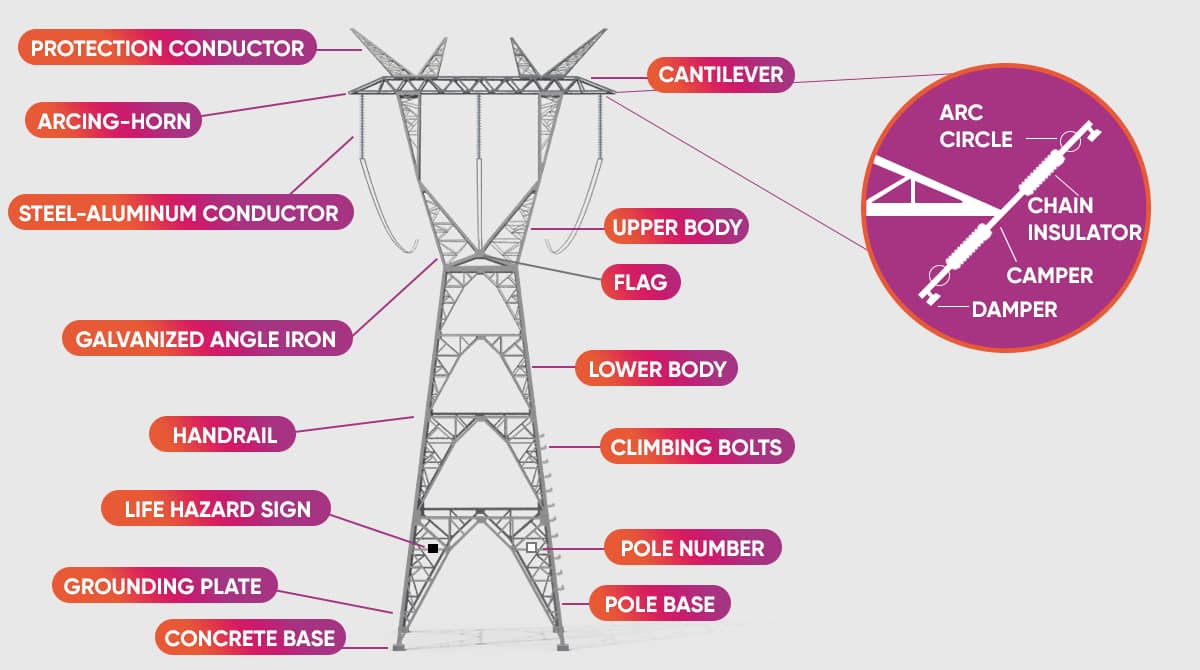
Characteristics of the Parts of a Utility Pole
A utility pole consists of complex parts that work in harmony with each other. To encapsulate these parts and their characteristics in a nutshell:
- Arcing-Horn: It ensures safer distribution of the electricity arc (when a high electric voltage is applied, the electric gap between two conductors is overcome by electric discharge in air, gas or liquid form).
- Arc Circle: Used in conjunction with the arcing-horn, it ensures that the arc is kept under control.
- Steel-Aluminum Conductor: A conductive material that enables transfer of energy inside the utility pole.
- Galvanized Angle Iron: A durable material used to shape the body of the pole.
- Cantilever: An attachment to which the conductor in the utility pole is attached to.
- Chain Insulator: An insulating part that prevents the electric current from flowing from the pole to the ground.
- Camper: Material used to connect the power lines to the utility pole.
- Damper: Material that prevents the conductor on the utility pole from swinging due to wind action.
- Upper Body: Located at the top of the utility pole to support the conductors on the pole.
- Flag: Prevents the conductor on the utility pole from rotating.
- Lower Body: Located at the bottom of the utility pole to make sure that the pole is firmly anchored in the ground.
- Climbing Bolts: Small attachments for climbing the utility pole.
- Handrail: Tiny materials used to ensure the safety of people working on the utility pole.
- Pole Number: Specific numbers assigned to utility poles.
- Pole Base: Materials used to connect the concrete legs of the utility pole.
- Concrete Base: The foundation on which the utility pole is grounded.
- Grounding Plate: Used to dissipate the electromagnetic currents on the utility pole to the ground.
- Life Hazard Sign: A warning sign that indicates that it is dangerous to work on a utility pole.
Types of Poles by Voltage Level
Electricity distribution networks have systems operating at different voltage levels. Therefore, different voltage levels require different types of poles.
What Are Low-Voltage Poles?
In general these are poles designed for voltages of 1,000 volts or less. These poles are used in electricity distribution systems for households and small businesses. Low-voltage poles are designed to place carriers on the pole and attach conductors to the pole.
What Are Medium-Voltage Poles?
Medium-voltage poles are usually designed for voltages of 1,000 to 69,000 volts. Medium-voltage poles are used in industrial facilities and distribution lines in large cities. These poles are larger and more durable because they operate at higher voltages.
What Are High-Voltage Poles? What Are High-Voltage Poles?
High-voltage poles are designed to withstand voltages ranging from 69,000 to 500,000 volts. These are used to distribute electricity over large areas, mainly used for inter-city power lines. High-voltage poles are larger and have greater strength.
-
Type T Poles
These feature a pair of cross arms attached vertically to the beams. They are suitable for Y or delta configurations. The load that T poles can carry depends on the length of the cross arm and the thickness of the material.
-
Type N Poles
These are one of the most commonly used high-voltage poles. Their distinctive feature is that they have an N-shaped beam. Such design provides a strong structure and high resistance. They are also made of high-quality steel or composite materials.
-
Type D Poles
These are an improved version of the steel T-pole. They are often used in the construction of high-voltage power lines, with a D-shaped beam connected by two pairs of cross arms. This design provides high strength and durability.
-
Type Z Poles
These are used in the construction of high-voltage power lines and have two Z-shaped beams. This design provides high strength and durability and better resistance towards wind loads.
Types of Poles by Material
Utility poles can be divided into several types, based on what material goes into constructing them. The most commonly used construction materials are the following:
- Iron Poles: Representing old-school utility poles, they are designed for low-voltage power lines. Low strength materials are usually used for the construction of such poles with a limited body height.
- Concrete Poles: Ubiquitously used in power transmission, concrete poles are made of durable and long-lasting materials. They are designed for high voltage power lines and stronger than poles made from other construction materials. The advantage of concrete poles is that they are durable and long lasting.
- Steel Poles: Steel poles are a preferred construction material for high-voltage lines. Thanks to their high durability, they can support heavy loads and have a long service life. Steel poles are also impact resistant and easy to install.
- Composite Poles: Composite poles, made of a combination of materials such as fiberglass, carbon fiber and epoxy resin, have a lightweight and strong structure. Their advantage is their robust structure and corrosion resistance.

Advantages and Disadvantages of Different Types of Poles
Poles come in different types and construction materials. Each type comes with its advantages and disadvantages. To give an example:
- Concrete poles can carry heavy loads due to their high strength, are corrosion-resistant and long lasting, but are difficult to transport and install because of their heavy weight, and their strength is lower than that of other materials.
- Steel poles can carry heavy loads due to their high strength, are impact resistant and easy to install, but they are prone to corrosion and do not last long.
- Composite poles are known to be light and strong. They are also corrosion resistant, but can be expensive and are more difficult to manufacture.
- T-type poles are easy to assemble and disassemble, lightweight and economical, but they are not suitable for high-voltage lines and are vulnerable to wind and storms.
- N-type poles can carry heavy loads thanks to their high strength. These poles are resistant to wind and storms, but difficult to install and relatively expensive.
- Type D and Z poles are easy to install, strong and durable, but difficult to transport and install due to their heavy weight. On the other hand, these poles are vulnerable to wind and storms.
What Are Different Types of Electrical Wires?
Electric wires are conductors used to transmit electric current. There are different types of electrical wires built for different purposes. Some common electrical wires are:
- Copper wires are widely used because of their high conductivity and durability. In addition, copper has the advantage of being corrosion resistant, able to withstand high temperatures.
- Aluminum wires are cheaper and lighter than copper wires, but have lower conductivity than copper and can break more easily.
- Steel wires are often used in power lines because of their high strength. In addition, steel wires have the advantage of being corrosion resistant.
- Copper-clad aluminum (CCA) wires are less expensive than copper wires. Also, they have higher conductivity than aluminum wires and are more corrosion resistant.
- Insulated wires are used for electrical connections, especially in households and offices. They consist of copper wires coated with PVC or other plastics.
- Fiber optic cables are used for high-speed internet and telecommunications services. They transmit information using light signals and can offer very high bandwidths.
How and How Often Should High-Voltage Poles Be Maintained?
 Maintenance of high-voltage poles is important to ensure a safe and healthy electricity transmission network. Maintenance extends the life of the poles, reduces the number of failures and ensures a safe working environment. Maintenance of high-voltage poles usually includes the following steps:
Maintenance of high-voltage poles is important to ensure a safe and healthy electricity transmission network. Maintenance extends the life of the poles, reduces the number of failures and ensures a safe working environment. Maintenance of high-voltage poles usually includes the following steps:
- Annual visual inspection and detection of breakdowns. During such inspections, deformations, cracks, corrosion and other damage to the poles are checked.
- High-voltage poles can become soiled by dust, dirt, leaves, and other external factors. Therefore, poles should be cleaned and cleared of moss and other plant material.
- The insulators of high-voltage poles are among the most important parts of poles. Therefore, care should be taken to ensure that the insulators are tight and have no cracks or other damage.
- Harpoons and clamps are used to attach high-voltage lines. These parts should be checked for looseness or damage and replaced if necessary.
- The grounding systems of high-voltage poles ensure safety in the event of a failure. Therefore, the grounding system should be inspected and repaired as needed.
Organizations Responsible for Power Transmission Lines
In Turkey, the operation of power transmission lines is usually the responsibility of TEİAŞ (Turkish Electricity Transmission Corporation) with construction works awarded to companies via tenders opened for transmission lines. These undertake the construction of poles by fulfilling the required conditions within the specified deadlines.
During these stages, the supply of materials and poles is carried out in accordance with TEİAŞ specifications. The expropriation of the land is carried out by the contractor company, which hands it over to TEİAŞ once construction is complete or the commitments only covers the construction works.
Interesting Information About Utility Poles
Many people find utility poles intriguing, often leading to queries such as the hissing of the poles, the balls on the installations and what happens to the birds that land on the wires. Let's have a look at some of the most intriguing aspects of poles.
Why Does It Sizzle on the Utility Poles?
Sizzles are usually caused by electrical discharges. The discharge occurs when air passes through a high-voltage electric field. The hissing noise often heard on utility poles is caused by the friction that occurs when molecules decompose and recombine as the air passes through a high-voltage electric field.
As a result of this friction, small explosions occur in the air and a hissing sound is produced. In addition, the effect of wind on the power lines, the friction of the cables against each other or the looseness of the connections can also cause a hissing noise. For this reason, hissing noises are more pronounced in power lines that are not maintained regularly or are poorly maintained.
What Is the Significance of Balls in Electrical Lines?
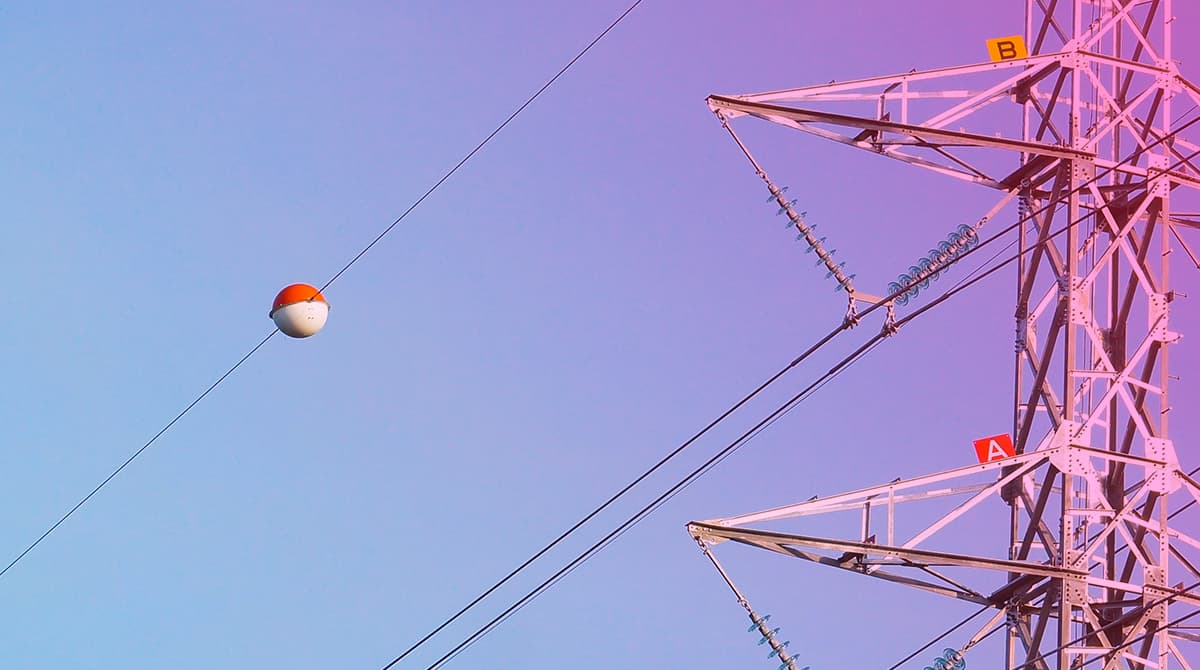 Balls in electrical lines are usually suspended on high-voltage lines and at certain distances along the line. These balls are used to prevent flying foreign objects from hitting the lines.
Balls in electrical lines are usually suspended on high-voltage lines and at certain distances along the line. These balls are used to prevent flying foreign objects from hitting the lines.
In addition, the use of balls can reduce the likelihood of deposits on the lines, such as ice or snow accumulation that can occur due to weather conditions.
In some countries, balls are also used to indicate the height of lines. In the United Kingdom, for example, the distance between the balls is in a certain ratio to the height of the lines, and this ratio is used to determine the height of the lines in places that are difficult to access for high-voltage lines, such as in forests or on farms.
Don’t Birds Landing on Power Lines Get Electrocuted?
 Birds landing on high-voltage power lines are usually not electrocuted. This is because of the low voltage and current strength of the electrical energy in the wires.
Birds landing on high-voltage power lines are usually not electrocuted. This is because of the low voltage and current strength of the electrical energy in the wires.
The voltage in power lines is usually only a few hundred volts, not thousands of volts. This voltage allows the birds' feathers to neutralize the electrical charge.
On the other hand, the distance between the legs of birds sitting on electrical wires is often as large as the insulating capacity of the wires. As a result, the electric current cannot flow across the birds' legs.
With high-voltage power lines, the electrical energy in the wires can be very high, which can electrocute birds. Therefore, with high-voltage wires, some precautions are taken to prevent birds from landing on the wires. For example, obstacles such as an insulator or bird wire can be placed on the lines.
What Happens When Electrical Wires Come In Contact With One Another?
When electrical wires get too close, a short circuit can occur, which can be dangerous. A short circuit is when the resistance of a circuit is too low and the electric current that should normally flow in a fluid circuit flows much more than normal.
For example, when two different wires touch on a utility pole, current flows directly between the two wires and the resistance of the circuit suddenly drops. The electric current cannot be regulated and there is a danger of overheating, fire or explosion. Also, safety measures such as circuit breakers or fuses may be triggered in the event of a short circuit.
Why Do Electrical Wires Sag in Summer and Tighten in Winter?
Electrical wires respond to temperature changes and can become shorter or longer. In summer, air temperatures rise, causing wires to lengthen. Therefore, the wires can appear slacker in summer.
In winter, on the other hand, the air gets colder and the wires stretch more. In cold weather, wires are less flexible and appear tighter. Therefore, wires may appear more stretched in the winter months.
Wet weather can also affect the tension of the wires. Rain or snow can increase the weight of the wires, causing them to sag more. Therefore, changes in electrical wire tension can vary depending on weather conditions, wire material and other factors.
Why Are Electrical Wires Buried Underground?
Electric wires can have many drawbacks when suspended in the air. Therefore, in some cases it may be necessary to ground the lines. Some reasons for burying electrical wires include the following:
- High-voltage power lines can be dangerous and pose a hazard to people and animals, especially when they are out in the open. Buried lines increase safety and prevent accidents.
- In some residential areas, overhead lines can be a visual nuisance. Underground cables can help the area have a more aesthetically pleasing appearance.
- Storms, high winds, and other natural disasters can damage electrical lines and cause power outages. Underground cables mitigate the impact of natural disasters and shorten the duration of power outages.
- Buried lines lose less energy than overhead lines. This increases energy efficiency and means less energy loss.
If you would like to learn more about utility poles, follow us and share your comments on the article.


 Online Services
Online Services Application Inquiry
Application Inquiry Pay Assurance Fee
Pay Assurance Fee Query Installation Number
Query Installation Number Compensation Fee Inquiry
Compensation Fee Inquiry Automatic Payment Order Inquiry
Automatic Payment Order Inquiry Partnership
Partnership

-Ssstem-nedir.jpg)



Leave a Comment