
What is in this article?
Did you know that seven different rare earth elements are used in smart phones, which are now an integral part of our daily lives?
Let’s take a closer look at the rare earth elements, which are used in small amounts in numerous areas but are of utmost importance as they are quite commonly used.
What Is a Rare Earth Element?
15 elements of the lanthanide series in the periodic table, as well as Yttrium and Scandium that demonstrate similar properties to these elements, are called the rare earth elements. Rare earth elements REE are also called green elements as they are used in developing environmentally friendly technologies.
Contrary to their name, rare earth elements are not rare to find. These elements are found scattered underground and in the form of various minerals. It is a demanding process to extract them from underground and process them. This is why they are called rare.
Using a small amount of rare earth elements in various alloys allows the resulting product to have additional reinforcement such as being more durable, resistant to fire, and an increase in magnetic properties. Playing a key role especially in development of technological products, rare earth elements are quite important sources for the future.
What are Rare Earth Elements?
Comprising of 17 elements in total, rare earth elements contain 15 lanthanides while the remaining two elements are Yttrium and Scandium.
Rare earth elements are split into two categories based on their presence in nature. Found more commonly in nature, Lanthanum (La), Cerium (Ce), Praseodymium (Pr), Neodymium (Nd), Promethium (Pm), Samarium (Sm) and Scandium (Sc) are classified as light rare earth elements.
Europium (Eu), Gadolinium (Gd), Terbium (Tb), Dysprosium (Dy), Holmium (Ho), Erbium (Er), Thulium (Tm), Ytterbium (Yb), Lutetium (Lu) and Yttrium (Y) are, on the other hand, called heavy rare earth elements as they are harder to find compared to the others.
Having silver and iron colors, these elements are interchangeable as they demonstrate similar properties. In elements with atomic numbers between 57 and 71 in the lanthanide series, the ionization energy increases as the atomic number increases. Many lanthanides have a specific color in ionic form.
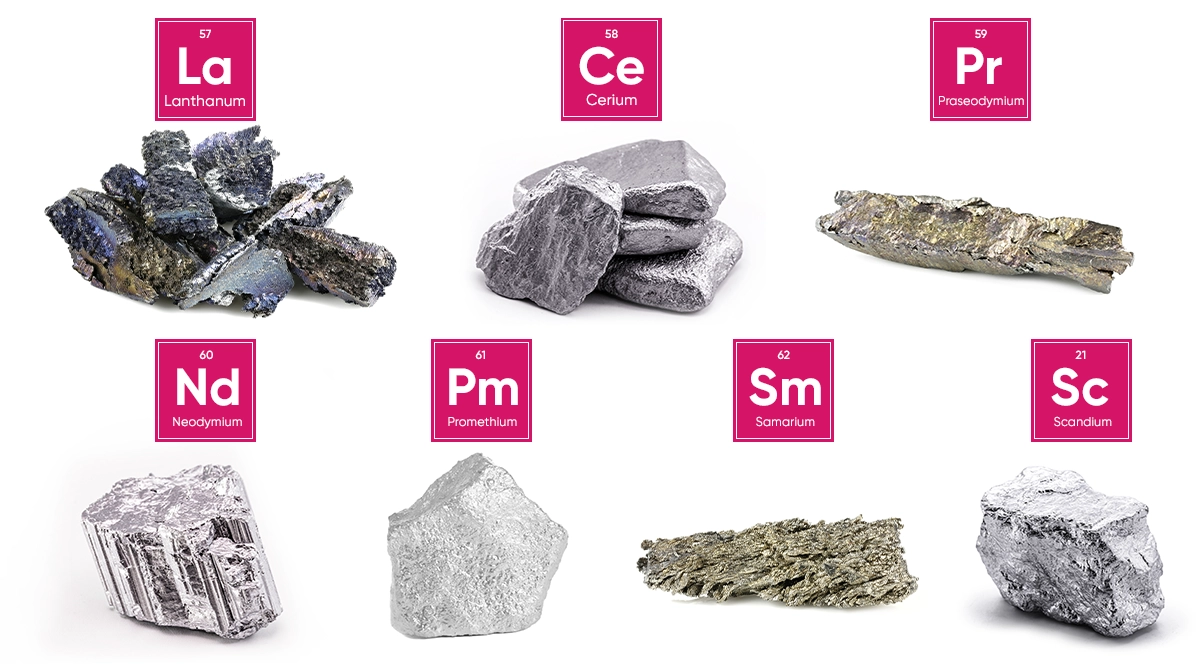

Lanthanum (La)
Atomic Number: 57
Found in solid state in nature, Lanthanum is used in photography, special glass production, telescope lens production, oil refineries and waste water treatment. Lanthanum also helps iron become more forgeable, thus it is frequently used in production phases.
Cerium (Ce)
Atomic Number: 58
With a shine similar to that of gloss, Cerium is used to give a yellow color to glass and ceramic and it is used as a breaking catalyst in oil refineries. Cerium is also used as a catalyst in exhaust systems to reduce emissions in automobiles.
Praseodymium (Pr)
Atomic Number: 5
Praseodymium is used in rare earth magnets, lasers, manufacture of welding goggles, coloring of glass and enamel products, firestones and durable metals prepared for planes.
Neodymium (Nd)
Atomic Number: 60
Neodymium is used in ceramic condensers, in processes to give a purple color to ceramic and glass, production of strong permanent magnets, infrared lasers, microphones, as well as computer and smartphone parts.
Promethium (Pm)
Atomic Number: 61
Promethium is the only element demonstrating radioactive property amongst rare earth elements. Promethium is usually produced artificially as it is almost never found naturally in earth. It is one of the rare earth elements used in the production of nuclear batteries and pacemakers.
Samarium (Sm)
Atomic Number: 62
Used in neutron capture studies and manufacture of lasers and magnets, Samarium is an earth element commonly used in the medical field. Samarium is used in cancer treatment, especially to fight prostatic, breast and lung cancer cells.
Europium (Eu)
Atomic Number: 63
Europium is used to manufacture fluorescent lamps, lasers, mercury-vapor lamps as well as red and blue phosphor production.
Gadolinium (Gd)
Atomic Number: 64
Gadolinium is used to manufacture magnets, glass with a high refraction index, magnets, X-rays and contrast media used for MRI.
Terbium (Tb)
Atomic Number: 65
It is used in manufacture of fluorescent lamps, green phosphor, colored screens, rare earth magnets and fuel cells. Terbium can be shaped quite easily.
Dysprosium (Dy)
Atomic Number: 66
Dysprosium is used in manufacture of lasers, lighting devices, computer parts and rare earth magnets, in addition to energy-efficient devices/appliances and nuclear reactors.
Holmium (Ho)
Atomic Number: 67
Holmium, which is an element that is quite strong magnetically, is mainly used to manufacture strong magnets comprising Holmium-containing alloys.
Erbium (Er)
Atomic Number: 68
Erbium is used in manufacture of the fiber optic technology and infrared lasers in addition to nuclear control rods.
Thulium (Tm)
Atomic Number: 69
Thulium is used in X-rays, in the defense industry and in the creation of various lasers in the medical field.
Ytterbium (Yb)
Atomic Number: 70
Used in flares for the defense industry as well as in manufacture of stainless steel and infrared lasers, Ytterbium is also used in nuclear medicine.
Lutetium (Lu)
Atomic Number: 71
Lutetium is one of the rare earth elements used in glass with a high refraction index and in tests used to determine the age of objects.
Yttrium (Y)
Atomic Number: 39
One of the rare earth elements that is not in the Lanthanide series, Yttrium is commonly used in LCD and LED screens as well as in camera lenses. Having a silver color, Yttrium is also used in the manufacture of lasers, spark plugs, anti-cancer drugs, surgical materials and high-temperature superconductors.
Scandium (Sc)
Atomic Number: 21
The light aluminum-scandium alloy manufactured using Scandium is often used in the aviation industry.
How Are Rare Earth Elements Produced?
The main challenge faced in extracting rare earth elements in surface mining, underground mining and solution mining is that these elements are found scattered and in the form of various minerals. Found in compounds with other elements, rare earth elements need to be broken up.
Rare earth elements are obtained by grinding, breaking, and using chemical and metallurgical methods. For this reason, having a reserve of rare earth elements is not enough. In order to make these different types of elements processable, it is necessary to have a separating technology specific to each element.

Properties of Rare Earth Elements
Rare earth elements are used in combination with various metals. Adding properties such as high durability to the materials they are used with, these elements reduce the ratio of the required metal, allowing to produce lighter and smaller products.
Often used in manufacturing the technology required to produce nuclear and renewable energy sources, rare earth elements are of critical importance in energy production.
In addition to energy production, it is quite important to have and be able to process rare earth elements used in communication tools such as satellites and smartphones, computer chips, medical devices and even in the defense industry. China, the largest rare earth element producer in the world, has taken advantage of this position and made great progress in technology manufacturing.
Uses of Rare Earth Elements
Today, the reason why rare earth elements are so important is that they provide additional properties such as high durability to the materials they are used with.
Rare earth elements are used in the production of electronics, energy, glass, magnetism, drugs, optics, ceramics and various catalysts. The fact that rare earth elements are used in so many different industries increases the interest in them.
-
Metallurgy
In metallurgy studies, rare earth elements are used to produce metals that are more suitable for production and use. Rare earth elements are used to create various non-steel and non-iron alloys.

-
Nuclear Energy Production
Rare earth elements are also used in processes that require high precision and durable products, such as nuclear energy production. These elements are used in radiation shields, reactor control, cathode ray tubes and strong magnet production.
-
Petrochemistry
In the petrochemistry industry, these elements are used in the manufacture of various catalyst products, especially oil refinement, cracking catalyst to break hydrocarbons, polymerization catalysts and oxidizing catalysts.
-
Ceramic Production
Rare earth elements are used in the manufacture of ceramic materials used in various fields. These elements are utilized in creating glaze, capacitors, fire-resistant refractor materials and coatings.
-
Glass Production
In glass and glass products manufacturing, rare earth elements are often used to manufacture optic glass, X-ray glass, pigments, glaze and glaze-coated products, infrared ray absorber, camera lenses and sunglasses.
-
Manufacture of Technological and Electronic Devices/Appliances
Playing a critical role in the manufacture of various electronic devices, rare earth elements are use in numerous fields from medical areas to manufacture of domestic appliances. Rare earth elements used in the production of superconductors are utilized to manufacture various products such as batteries, lamps, smartphones, computer chips, microwave crystals, medical lasers and dental porcelain.
In addition to all of these categories, rare earth elements are also used to in cryogenic cooling, solar power, jewelry and textile production. When these areas of use are found together, the importance of rare earth elements become even more visible.
Used both in superconductor production and cryogenic cooling, rare earth elements are utilized in the manufacture and use of extremely strong superconducting magnets. Therefore, they play a critical role in the manufacture of high-technology devices such as MRI devices and maglev trains. Similarly, the use of rare earth elements in wind turbines and solar panels in addition to the manufacture of batteries and electrical vehicles put these elements in a critical position in the generation and use of renewable energy.
Rare earth elements contribute to developments such as the fiber-optic technology, fluorescent lamps and MRI devices, which are amongst the quantum mechanics applications.
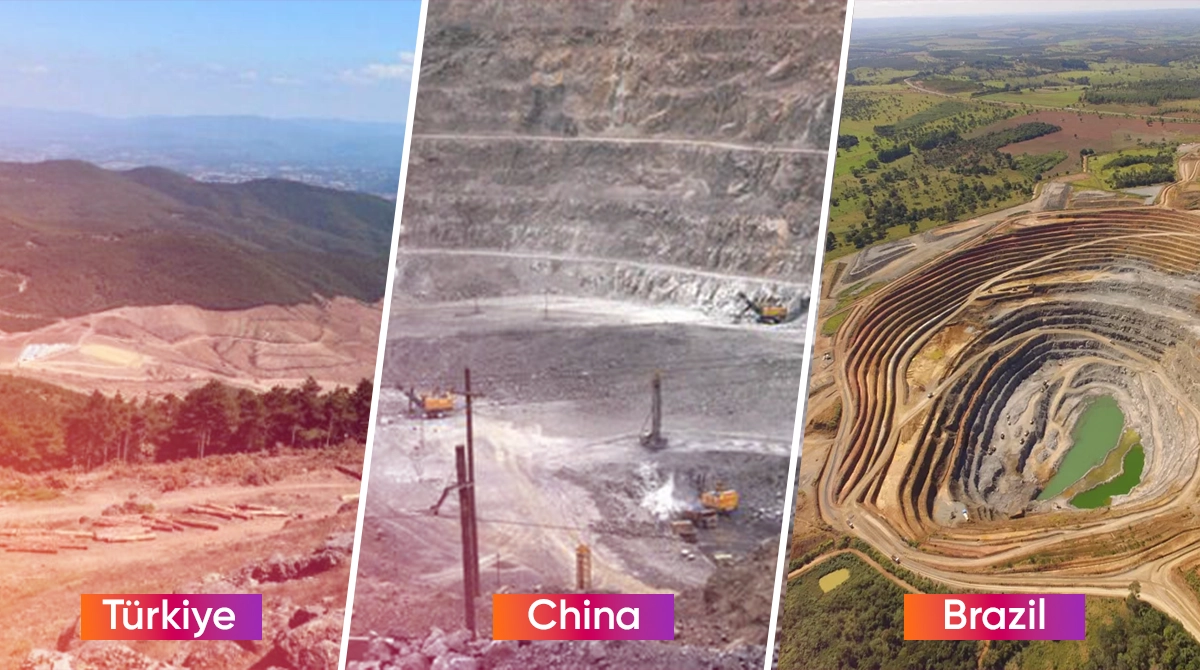
Reserves of Rare Earth Elements in the World and in Türkiye
Rare earth elements are found quite commonly on Earth. China is the world’s leader with regards to the reserves and processing of rare earth elements. Chine has almost 36% of all the reserves known in the world, followed by Brazil and Vietnam.
As for Türkiye, the research in the Kızılcaören complex in Eskişehir is quite promising in terms of rare earth elements reserves. In these researches, NEE and torium sources were found in the region. In said area, fluoride-barite-NEE mineralization formed through hydrothermal solutions was found.

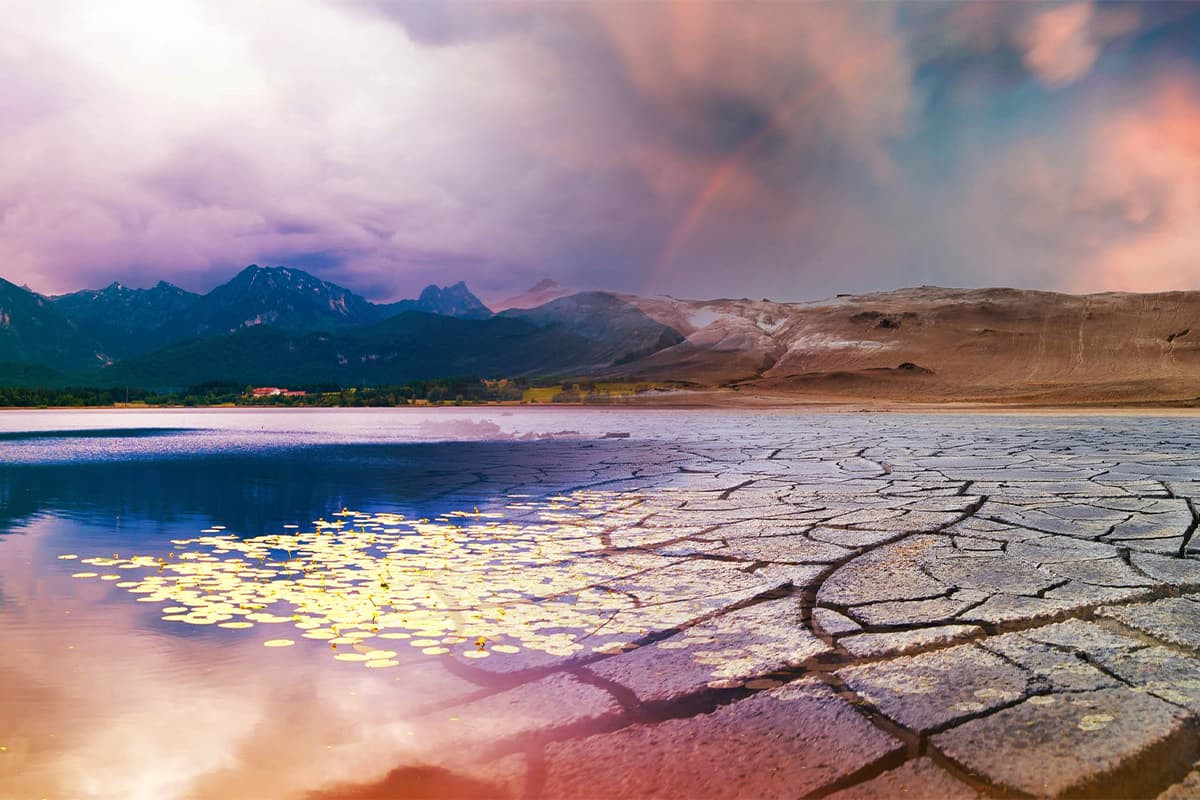
Environmental Effects of Rare Earth Elements
Rare earth elements are not only a keystone for high-technology products but also green energy systems. We can even say that this is the reason rare elements are also called green elements to summarize their positive effects on the environment.
When we take a closer look at their environmental effects, we can see that rare earth elements play a key role especially in the manufacture of wind turbines. This alone helps reduce the need for fossil fuel and fight climate change.
Obviously, this is not the only reason rare elements are so important in today’s world. This type of elements also play a critical role in the manufacture of modern technology devices. Widely used in satellites, smart phones, televisions, MR devices, other devices equipped with magnets, electrical vehicles, batteries and many other areas, they allow these products to be manufactured more efficiently and with additional performance. This way, they help reduce the negative environmental effects caused by the manufacturing process.
Production of rare earth elements, which is practically a horse race amongst countries, is vital for the technologies of today and the future. Although they are used in small quantities, this causes them to become more common, hence an increased interest.
Don’t you think that the solutions that will help the development of humanity and technology are still waiting to be accessed underground? Don’t forget to share your thoughts with us.


 Online Services
Online Services Application Inquiry
Application Inquiry Pay Assurance Fee
Pay Assurance Fee Query Installation Number
Query Installation Number Compensation Fee Inquiry
Compensation Fee Inquiry Automatic Payment Order Inquiry
Automatic Payment Order Inquiry Partnership
Partnership





Leave a Comment