
What Is Wind Power? How Do Wind Turbines Generate Energy?
What is in this article?
One of the renewable energy sources that have started to replace fossil-based energy sources, wind power is a clean and sustainable type of energy.
Wind turbines meet some of the electricity needs thanks to the ever-increasing number of studies in Turkey, as is the case with the rest of the world.
In this article, you will find out all details on wind power and types of plants, as well as their electricity production capacity.
What Is Wind Power?
 Wind means air motions formed by the forces that are created as a consequence of the sun heating the earth unequally and pressure differences. The motional energy that this air stream has is called the wind power.
Wind means air motions formed by the forces that are created as a consequence of the sun heating the earth unequally and pressure differences. The motional energy that this air stream has is called the wind power.
The kinetic energy that the air mass has is converted into mechanical energy. In this regard, wind power is also considered as transformed solar power. On average, 2% of the sunbeams reaching the earth becomes wind power.
Dating back before the common era, this energy is the starting point of mills and windmills on land, and of sailboats in the sea. Wind power was first defined by Hero, a Greek engineer.
Wind power was first used in the Middle East in 2800s B.C., and there is evidence that it was used in Mesopotamia and China in the 17th century B.C.
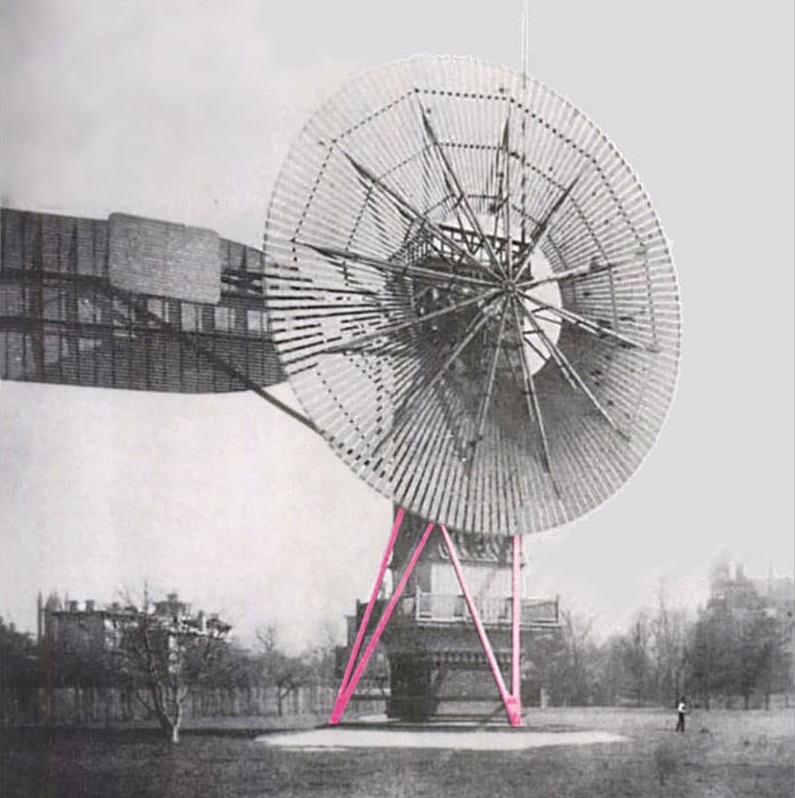 The very first windmills were installed in Alexandria before they were used by the Persian and Turks in the 7th century B.C., and by Europeans starting from the Crusades.
The very first windmills were installed in Alexandria before they were used by the Persian and Turks in the 7th century B.C., and by Europeans starting from the Crusades.
Europeans had already started using windmills commonly before the Industrial Revolution, with 10,000 windmills in the Netherlands before the 19th century began.
However, steam-generated machinery caused wind power to become less important.
The first modern wind turbine was invented in 1887 by Charles F. Brush from the USA.
Wind power became increasingly important after the 19th century. Today, more and more studies are being conducted every day in this field both in Turkey and around the world.
How Is Wind Formed?
Sun beams cause heating on the atmosphere. As the air is heated, its density drops, causing the air to raise and be replaced by cold air. Earth’s rotation combined with this cold air creates an air motion that has a high level of kinetic energy.
There are some factors inside the atmosphere, which creates the wind and wind speed. These include centrifugal force, pressure gradient force, fractional force and Coriolis force.
Wind is a motion of air spinning around a center. During this rotation, the air is impacted by the centrifugal force, which forces it to move away from the center.
Frictional force, on the other hand, does not have any contribution to wind formation but it reduces speed. When it is closed to the ground, it is pushed upwards although it has more effect due to turbulence.
Frictional force can decelerate the wind at heights up to 600 meters approximately. Gradient force forces the air to go from high pressure to low pressure, while the Coriolis force causes deflection.
What Is a Wind Turbine?
A wind turbine transforms the kinetic energy to mechanical energy before converting it into electrical energy.
Wind turbines are categorized based on their axes, power, speed, number of blades, existence of a gear, and location of installation.
The first turbine models installed were quite bulky and noisy, while today’s modern turbines have lower levels of noise.
Countries should invest in turbine technologies so that they can benefit from the existing wind potential to the desired extent.
Parts of Wind Turbines
The parts of a wind turbine are as follows:
- Wheel blades
- Control unit
- Gearbox
- Tower
- Wheel
- Generator
- Low and high speed shaft
- Machinery section
- Stop arm
- Anemometer
- Deflection drive
- Deflection engine

-
Horizontal Axis Turbines
 A horizontal axis wind turbine is comprised of a base, rotor blades, a generator, tower and engine sections. The base supports the tower to help it stay steady.
A horizontal axis wind turbine is comprised of a base, rotor blades, a generator, tower and engine sections. The base supports the tower to help it stay steady.
Tower, on the other hand, supports both the rotor hub and the body. For this reason, durable materials such as concrete and steel are used to make towers.
Towers may have pipes, inclination or cages to reduce turbulence. Rotor shaft and power generator are found at the top of the tower.
Most horizontal axis turbines are equipped with three blades. The number of blades, however, may vary. There may be an odd or even number of blades, sometimes more than three.
The number of rotor blades also affect the rotating speed; less blades equals higher rotor speed. A gearbox is used to accelerate the rotation of blades.
Blades are usually located 20 to 30 meters from the ground and higher than the obstacles around. The efficiency obtained from these turbines are 45% on average.
Horizontal axis turbine is the most common wind turbine type globally. This model is frequently preferred for land, ocean and the sea.
It can also be convenient for harsh winter conditions. For this, systems are established to keep turbines warm.
-
Vertical Axis Turbines
In vertical axis wind turbines, blades are located vertically, which means the direction of rotation is vertical to the wind direction.
There are no guiding parts as the turbine is not affected by the changes in wind direction. Furthermore, no tower is needed as the gearbox and generator are located on ground level.
These turbines are categorized in two groups, i.e. Savonius and Darrieus. Darrieus turbines are categorized in three groups: H-Darrieus(h-rot), Helisel Darrieus and D-Darrieus.
The Darrieus turbine was invented by Georges Jean Marie Darrieus in 1925 and patented in 1931.
Darrieus turbines have slightly inclined blades to minimize tensile stress. These models require a drive motor for the first motion and are usually equipped with two or three blades.
H-Darrieus, on the other hand, is different from Darrieus turbines as it has pitch control applied on the blades and has a flat aerodynamic form.
Centers of Savonius turbines are in a leaning position, symmetrical to each other. It is comprised of two half cylinders that are placed between two horizontal discs and also called blades.
Savonius wind turbines were invented in 1925 by Sigurd Johannes Savonius.
When Darrieus and Savonius models are compared, Darrieus models are more advantageous in that they consume less energy. On the other hand, Savonius turbines also offer benefits as they can start automatically. Gambier, an academic, stated that it would be ideal to benefit from both models.
How Do Wind Turbines Work?
Unlike ancient windmills, a modern wind turbine does not rely only on the power of the wind, but also on the principles of aerodynamics to move the blades.
We can also mention some aerodynamic forces that run the rotors, which convert kinetic energy into mechanical energy. These are the drag force and buoyant force.
The aim is to ensure that the moving air rotates the blades. Once the wind touches the blades, a pressure difference is created and the blades rotate.
Is There a Wind Turbine for Homes? How Much Electricity Does It Generate?
Electricity generation capacity of household wind turbines depends on the wind in the region. Although these turbines can generate enough electricity to meet the needs of a house, it is recommended to use the turbine together with a storage system or other power generation systems to ensure that the power does not go off when there is no wind.
-
What Power Tools/Appliances can be Used with a Wind Turbine for Homes?
A turbine that works with enough power for a household means uninterrupted operation of all electrical products at home, such as the lamps, refrigerator and washing machine.
-
What Materials are Needed for a Wind Turbine for Homes?
The materials required to make a turbine at home include a grinding machine, pipes suitable for the size of the turbine, a generator motor, a welding machine, screws, a drill, wooden plates, a pillar, and a template that shows the drawing.
How Is Wind Converted into Energy?
 To convert wind into energy, first of all, you need to determine geographically efficient areas that have high level of winds.
To convert wind into energy, first of all, you need to determine geographically efficient areas that have high level of winds.
Then, you need to calculate the maximum energy that can be generated from that area to determine the number of turbines required.
Once the wind turbines are installed, blades start to rotate with the air motions. These blades rotate the wheels based on the number of cycles.
Energy is generated through rotation of the wheels. This energy can either be stored in generators or transferred to transformers for use.
How Much Energy Can Be Generated Using Wind Power?
Considering that the electricity generation capacity of wind power is 1 MW, approximately 3 MW electricity can be generated annually. For example, a turbine with a 10 kW capacity can generate around 16,000 kWh. In the United States of America, the electricity consumed by one house was found to be 10,000 kWh per year. In this case, a turbine with a 10 kW capacity can easily meet the needs of a household.
Under ideal conditions, a large wind turbine can generate 1.8 MW electrical energy, which is enough for around 600 households.
Areas of Use for Wind Power
Wind power is used as follows:
- Wind power can be used for agricultural water pumping and grains grinding. Examples include some facilities found in Urla and Balıkesir in Turkey.
- Electricity needs of industrial plants can be met with wind turbines outside the grid.
- Wind power is one of the efficient sources for water mains. The need for storing water can be met with the energy obtained from turbines. In this context, it can be used at water treatment plants and at facilities that produce potable water.
- Although wind power has limited use at homes, it can generate enough power to meet the needs of a household.
- Wind power can be utilized for garden lighting, logistics, battery and charging systems, and cooling processes.

What Are the Advantages of Wind Power?
Advantages of wind power are as follows:
- The most important advantage of wind power is that it is an infinite, domestic and clean energy source. It not only creates zero negative effects for the environment, but it also minimizes the carbon dioxide and greenhouse gas emissions caused by fossil fuels.
- It eliminates dependency on foreign resources. It creates job opportunities in the country to operate wind turbines.
- It is easy to install/uninstall and maintain these turbines. A land with an uninstalled turbine can be reused.
What Are the Disadvantages of Wind Power?
Disadvantages of wind power plants include the following:
- Although wind turbines of 30 to 40 years of age can be used without any additional costs, it is expensive to build a new turbine.
- Unit capacity of wind power is quite low. On average, only 30% of the energy capacity can be used.
- In order for the electricity generated from wind power to be continuous, it may be required to integrate the wind power plants with hydraulic or thermal power plants, or create storage areas for them. Because when the wind stops, so does the production. It is compulsory for wind turbines to be connected to a grid, and a transformer is required for each turbine.
- Wind turbines could be dangerous to the wild life. It is a known fact that flying animals sometimes hit the blades and die.
|
Traditional colors for wind turbines are white and grey, which has always been a source of attention for bugs. Moreover, bats and birds that want to eat the bugs around the blades hit these blades and face the risk of death. A study by the European Journal of Wildlife Research revealed that purple is the color that attracts least attention from bugs. Aydem Renewables has conducted extensive studies to prevent bat and bird deaths through ornithological (birds) and mammological (bats) monitoring at the company’s wind power plants. As a result, Aydem Renewables painted the wind turbine blades purple, which allowed the company to prevent bat and bird deaths. |
Turkey’s Potential for Wind Power
According to the Wind Power Potential Atlas (REPA) created by the Ministry of Energy and Natural Resources, the total wind power potential in Turkey was found to be 47,849.44 MW. This potential corresponds to 1.30% of Turkey’s total surface area.
In Turkey, it is possible to install wind turbines with a 5 MW power per kilometer in areas that have a wind speed at or above 7.5 m/s and are located 50 meters from the ground. This value is determined using the micro-scale wind flow model and the medium-scale numerical weather forecasting.
Licensed wind energy installed power is 10,533.90 MW for 2021. The share of this installed power in the overall electricity production is 11.42%. Furthermore, the number of licensed wind power turbines increased by 39 year-on-year and reached 204.
-
How Much of the Overall Energy Needs Are Met Through Wind Power in Turkey?
Turkey uses wind power to meet some of the overall electricity generation, and this amount increases every year.
It was 0.04% in 2004 but it reached 9% by 2021. Efficiency is increased with the increasing investments and the wind turbines becoming more functional thanks to new technologies.
Turkey’s Wind Power Map
The Marmara Sea and the Mediterranean and Aegean coasts are among the regions with the highest potential for wind power not only in Turkey but in the whole world.
The area surrounding Çanakkale, as well as Bozcaada and Gökçeada, Urla, Sinop, Datça and Bodrum are also convenient for wind power generation. The wind potential in Gökçeada in particular is equivalent of the Danish coasts and
Southern England. It has a higher potential than the Adriatic coasts. Other than this, the Southeastern Anatolian Region and the Northern Anatolian Hills also have high potential.
Wind Power in the World
Today, more than 100 countries benefit from the wind power. On a global scale, Europe, North America and Asia are the continents with the most installed power for wind.
Among the countries that benefit the most from wind power plants and conduct studies in this area are India, Denmark, Germany, Spain and the USA. However, in 2022, China has become the country that uses the wind power most through the investments made.
Important Wind Power Plants in the World
Investments in clean energy are quite important in China, where air pollution is a serious problem. Located in the Gansu state with an 8 GW capacity, the Gansu Wind Farm is home to the biggest turbines in the world. This farm can generate electrical energy that would be enough for a small country. However, majority of the energy generated at this plant is not used due to low demand.
Located in India, the Muppandal Wind Power Plant comprises 3,000 turbines and has a capacity of 1,500 MW, using the high energy potential in that region. The largest land plant in the country, on the other hand, is the Jaisalmer Wind Power Plant. This plant uses small and big turbines and has a 1,065 MW capacity to produce clean energy.

In the USA, Alta Wind Power Center is the largest plant in North America. Located in an area of 3,200 acres, this plant works with a 1,548 MW power capacity.

Is Wind Power Expensive? Comparison with Other Energy Sources
Wind power costs are high at the installation stage. After installation, however, the cost per MW for the electricity generated drops because no fuel is used and there are no operating expenses.
When determining the cost, one needs to consider the electrical energy generated per year and the initial cost of the plant. Unit cost and sales prices, transport, type and size of the turbine, inflation, legislations and environmental impacts must also be considered when calculating the cost.
Renewable energy sources include wind power, solar power, biomass power, hydraulic power, geothermal power and wave power. These sources started to replace fossil fuels between 2010 and 2020, with solar power and wind power plants having the costs that have dropped the most.
More investments are made every year in these sources that offer an alternative way to generate electrical power with lower costs. The fact that renewable energy sources are more economical and environmentally friendly makes them more preferable.
How to Get a Wind Power License
Companies should first apply for a preliminary license to install a wind power plant and produce electricity.
If a company meets the criteria required for the preliminary license, it can get a production license. At this time, it can complete the permission procedures and start producing power as per the Law No. 6446.
The process to get a license is as follows:
- Establishing a company as per the Turkish Code of Commerce to produce electricity
- Getting the use rights for the work field
- Installing wind measurement stations
- Having the Measurement Station Installation Report approved by the Directorate General of Meteorology, and sharing such data for at least one year
- Preparing the documents required by EPDK (Energy Market Regulatory Authority) and applying for a preliminary license
- Technical assessment by the Directorate General of Energy Affairs and reporting to EPDK
- Getting the production license
What Is Licensed and Unlicensed Wind Power Investment?
Licensed and unlicensed wind power investment (WPP) states which production is to be performed licensed or unlicensed as per the Electricity Market Law No. 6446. In licensed WPPs, the electricity produced is provided to consumers through national channels, while in unlicensed WPPs, production has defined limits.
Let us know what you know about wind power in the comments, or ask us what you’re wondering.

 Online Services
Online Services Application Inquiry
Application Inquiry Pay Assurance Fee
Pay Assurance Fee Query Installation Number
Query Installation Number Compensation Fee Inquiry
Compensation Fee Inquiry Automatic Payment Order Inquiry
Automatic Payment Order Inquiry Partnership
Partnership







Leave a Comment