
How does a Battery Work? Facts About Batteries
What is in this article?
Batteries, which are portable energy storage devices that we use in many devices in our daily lives, are divided into different groups. Batteries are divided into two groups: rechargeable and disposable, and are also classified according to the materials used in their production and the size and shape they have.
How do batteries work? When was the battery invented? How should batteries be recycled? Answers to these and similar questions can be found in our article.
What is a Battery?
Non-stationary energy storage devices that work on the principle of converting chemical energy into electrical energy are called batteries. Batteries are divided into two main groups: primary, meaning they can be used once, and secondary, meaning they can be used multiple times by recharging.
Disposable batteries are commonly used in low-power devices, such as children's toys and flashlights. But rechargeable batteries are more commonly used in technical devices that consume a lot of energy, such as photo and video cameras.
What are Types of Batteries?
In addition to rechargeable and non-rechargeable battery groups, batteries are also classified by the materials used in their manufacture.
For example, in the disposable (primary) battery group, there are products containing zinc, manganese, carbon-silver oxide, mercury, and lithium. Batteries from zinc-carbon, lithium, alkaline. etc. are made using these materials.
In the group of secondary batteries called rechargeable batteries, lead, nickel, sodium, iron, and lithium materials are predominantly used, and battery types labeled lithium-ion, lead-acid, lithium-polymer, and nickel-iron batteries are manufactured.
Another method of classifying batteries is based on battery size. In this classification, battery types such as AA, AAA, button, C, and D stand out. AA and AAA batteries can be said to be the most commonly used group; they are often preferred for operating devices such as remote controls.
Button batteries are generally used in devices such as calculators and wristwatches. The C and D battery types are similar to the AAA and AA batteries, but have a higher power rating.
How and When Was the Battery Invented?
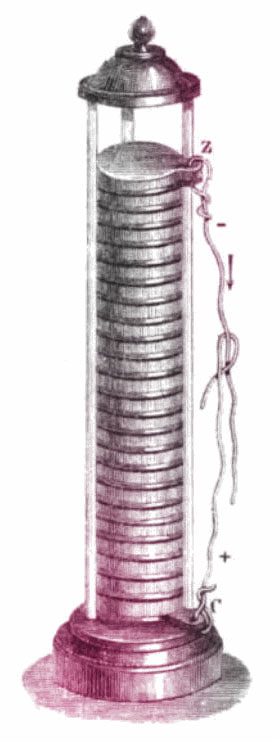
History of batteries dates back to animal experiments conducted by Italian physicist and biologist Luigi Galvani in the 18th century. Galvani's experiments paved the way for the invention of the battery.
Physicist and chemist Alessandra Volta conducted experiments that used Galvani's findings. Unlike Galvani, he did not use animals, but only the conductivity of materials such as damp cloth and metal to conduct experiments that enabled him to produce batteries.
The first battery was developed by Volta, but the British chemist and physicist John Frederic Daniell took battery manufacturing a step further in the 1800s, making it possible for batteries to become the parts that powered devices such as doorbells, telegraphs, and telephones.
In the 1900s, the work of American inventor Thomas Edison began to attract attention. Edison, who claimed to have developed the iron-nickel battery, suddenly found himself in limelight.
In 1912, chemist Gilbert Newton Lewis produced the first lithium-ion battery. Today, lithium-ion batteries are among the most widely used, powerful, and long-lasting batteries.
Battery Structure and Operation
Different types of batteries contain different parts. Nickel batteries, used in devices such as cameras and cordless phones, contain parts referred to as gasket, positive and negative terminals and electrodes, a separator, and a jacket.
The type of lithium-ion battery used in cell phones also contains these parts plus the degassing valve. With lithium polymer batteries, there are no negative and positive terminals and electrodes. There are only laminated foils, lithium conductors and graphite conductors. This type of battery is also used in cell phones.
Zinc-containing batteries contain positive and negative elements, a gasket, a separator, an adhesive sealing film, and a membrane. This type of battery is also commonly used in hearing aid.
-
Markings on the Battery and Their Meanings
There are many different markings on batteries; these are listed below according to their intended use:
- Battery type markings (Li-Ion, Al-Mn, etc.)
- Markings indicating the capacity of the battery (mAh)
- Abbreviations indicating the quality standards of the battery (REACH, RoHS)
- Marks indicating the operating voltage of the battery, and how many volts it is (+ and -)
What Does the Battery Life Depend On?
Disposable batteries, which are not rechargeable, have a certain life span. The useful life varies depending on the material used and the quality of the battery. It is not possible to affect the life of products in this battery group.
The life of batteries of the rechargeable group is directly affected by use. Reusable batteries have a certain re cycling, i.e. charging and discharging capacity. The remaining battery life can be calculated by considering the battery as charged even if it is not fully charged, and used even if it is not used until it is fully discharged.
How Is the Battery Manufactured?
Many different materials can be used to make batteries. However, regardless of what chemicals are preferred, conductive parts must be present.
This part, which can be in solid or liquid form, is a basic component of any battery. Batteries are made by combining other parts such as negative and positive terminals, separator and jacket as needed.
How Is the Battery Charged and Does It Continue to Function When Charged?
Rechargeable and reusable batteries can be recharged and reused many times, even hundreds and thousands of times.
The basic principle of charging batteries is that they respond to the opposite energy input. Batteries charged by reverse reaction can be used repeatedly.
Scope of Use of Batteries
 Batteries are used in homes, hospitals, schools, and offices to power various devices. Chargeable batteries are used to power laptops and cell phones.
Batteries are used in homes, hospitals, schools, and offices to power various devices. Chargeable batteries are used to power laptops and cell phones.
With devices such as cordless phones and radios, which are still found in some homes, schools, and workplaces, disposable, high-power alkaline batteries are generally preferred.
The portability of the ECG machine in hospitals, so that it can be taken with the patient, is due to the use of batteries. Rechargeable lithium-ion batteries are generally used in these devices.
In addition, the energy of devices that serve very different purposes in all walks of life-from electric toothbrushes to drones, from hearing aid to wristwatches, from cordless vacuum cleaners to kitchen scales-is provided by batteries.
Today, electric vehicles, offered as a clean alternative to gasoline-powered cars, also use rechargeable lithium-ion batteries.
6 Things to Consider When Using Batteries
Below we have listed the things to look out for when using batteries. By keeping these in mind, you can ensure that the batteries used to generate power will last longer and contribute to power savings.
- Before inserting batteries into a device, you can make sure that the battery slot and electrically conductive contacts are clean.
- Rechargeable batteries should only be charged with their own chargers, otherwise dangerous situations such as swelling or even explosions may occur.
- You can make sure that the batteries are not in a very hot or very cold environment during charging.
- If you expect that you will not use the batteries for a long time, you can remove them from the device, wipe them carefully with a dry cloth and store them at room temperature in a package or box.
- If you refill Ni-Cd and Ni-MH batteries only when they are fully discharged, they will last longer.
- It is important to make sure that the energy of lithium-ion batteries does not drop to a very low level, and to charge them when they are at 50%.
What Is a Waste Battery?
Batteries that have finished their useful life, and have reached their maximum number of cycles when they are charged and if all the energy in them has been consumed, providing they are disposable batteries, are called waste batteries.
The recycling of waste batteries is of great importance so as not to pollute the environment. Waste batteries that are not recycled can produce harmful emissions or leach heavy metals into soil and water. To prevent this, the recycling of waste batteries must always be a priority.
In addition, when waste batteries are recycled, the valuable materials they contain can be reused and the industry can benefit economically in the production of new batteries.

-
How Can You Recycle Used Batteries?
Batteries play an important role in the rise of renewable energy, as they can be used instead of fossil fuels to generate energy. In this regard, batteries should be properly recycled when they can no longer be used.
While users cannot recycle their batteries themselves, they can collect used batteries in a closed box at room temperature at home and throw them in the used battery box.
If you too support nature with recycling, you can let us know in the comments what methods you use for your waste batteries.


 Online Services
Online Services Application Inquiry
Application Inquiry Pay Assurance Fee
Pay Assurance Fee Query Installation Number
Query Installation Number Compensation Fee Inquiry
Compensation Fee Inquiry Automatic Payment Order Inquiry
Automatic Payment Order Inquiry Partnership
Partnership





Leave a Comment