
Is Wireless Power Transmission Possible? How Is Power Transmitted Wirelessly?
What is in this article?
The question of whether wireless power transmission is feasible arises as technology develops. Everyone wants to get rid of the cable system that links electricity-generating plants to electronic devices. But is it really possible to do this?
The typical response is that yes, it is possible to transmit power wirelessly. But things are still quite limited right now. Radio frequency identification tags or satellite communications have both employed wireless power transmission, or WPT for decades.
But is it also applicable to daily life?
Consider how much nicer cities would seem if electrical lines on the streets were eliminated. Picture being able to access power wherever you want, including at home. Despite sounding like a concept from science fiction movies, wireless electricity has been used in some places. Wireless power has been a recurrent concept since Tesla, despite sounding like a fascinating and future idea.
The remainder of the post will delve into the specifics of wireless electricity transfer and address any questions you may have.
What Is Wireless Electricity?
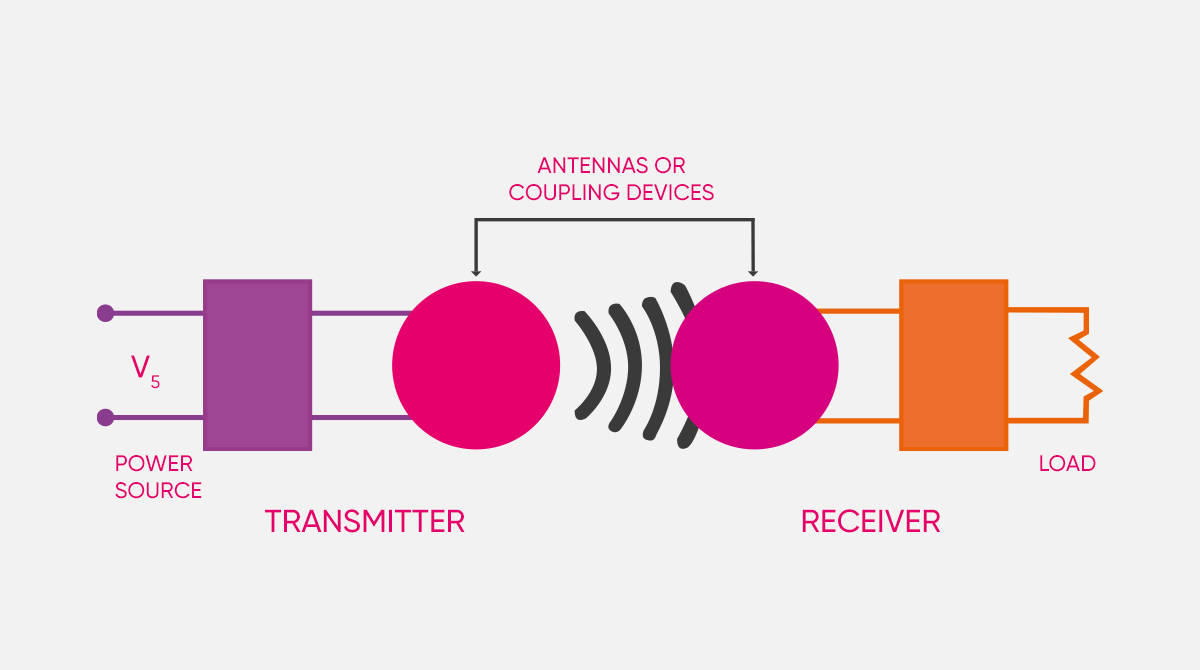
Before we get into the topic, let's first explain what the concept of wireless electricity is. Wireless electricity transmission is a system that allows electricity to be transmitted without wires. With wireless transmission, electricity is transmitted from stations to consumers without using poles or transmission lines (cables). Wireless power transmission (WPT) generally refers to the process of transferring electricity from the power source to the electrical load through induction coils across an air gap.
 The electromagnetic induction theory underlies the operation of wireless power or power transfer. The principle of electromagnetic induction or the production of an electromotive force by a moving magnetic field summarizes it. In essence, the transmitter connects to the receiver generating current instead of cords.
The electromagnetic induction theory underlies the operation of wireless power or power transfer. The principle of electromagnetic induction or the production of an electromotive force by a moving magnetic field summarizes it. In essence, the transmitter connects to the receiver generating current instead of cords.
Solar power can now also be used to produce power. The idea of using the sun to generate electricity first appeared in the 1970s. Solar satellites generate electricity through solar panels. A transmitter is used to transfer the electricity produced.
With wireless electricity, there is no need for physical connections because the energy is transmitted utilizing a unique technique. Without a cable connection, the receiver and transmitter perform the conversion process. Wireless electricity transmission is made feasible by the magnetic induction that takes place between the receiver and the transmitter. Wireless power transfer is made possible by the electromagnetic field that is created between the two locations.
Wireless electricity is one of Tesla's greatest dreams. Tesla wanted to transmit electricity wirelessly to all parts of the world and make energy a resource accessible to everyone, thus laying the foundation for wireless power transmission.
How Does Wireless Power Transmission Work?
One of the biggest problems with power grids is that electrical power suffers various losses during transmission. The resistance of the system's wires is one of the main reasons for power loss during transmission.
Wireless power transfer is a notion that Nikola Tesla first proposed in 1899, and it has continued to evolve ever since. Then, how is wireless power transfer carried out in practice?
The transfer of electricity without connection to an electrical load is what wireless power transmission is, in general. It has many advantages such as reliability, speed, low maintenance cost and efficiency.
One of the ideas to be mindful of is resonance. Systems oscillate at a specific frequency and wave width due to resonance. The fundamental tenet of wireless power transmission is that energy can be exchanged between two objects by virtue of proximity or resonance. This method can be used to wirelessly recharge computer batteries and charge smart devices, among other things. Additionally, if a system is galvanically isolated, it lowers the chance of electric shock. Electricity flows in the same direction and with the same amount of force when there is galvanic current. Galvanic isolation describes a partial interruption of the electric current.
Since wireless power transmission is a new technology, a wide range of techniques can be created as distances widen.
Inductive power is produced through wireless power transmission by using the magnetic field that is sent from the transmitter to the receiver. Power transmission results from the transmitter's unique components converting the direct current the power source emits into alternating current.
Nikola Tesla and the Dream of Wireless Electricity
In his prime, Nikola Tesla was driven by a concept and did everything in his power to further it. He postulated that electricity may travel great distances. However, Tesla's dreams for wireless transmission of power across the world were never achieved.
Tesla's dream was to transmit electricity free of charge via towers that surrounded the entire world and to facilitate the exchange of information.
Nikola Tesla built the first of these towers on Long Island in 1901, taking the first step toward realizing his dream. With this tower, he intended to demonstrate that information could be transported across the ocean and that power could be transmitted similarly, but as he worked to make this innovation a reality, he was cut off from funding, and the project was shelved. He was unable to accomplish his goal because he lacked sufficient finances.
The Tesla coil, an innovation of his, however, gave rise to an image of wireless electricity.
Even though Nikola Tesla partially fulfilled this concept, why do we still not have wireless electricity in our homes?
Electricity or energy needs certain means of transportation, such as cables. Cables create a pathway for this transmission. Despite the fact that it is technically possible to do away with cables, this technique is currently only effective across extremely limited distances. Consider wireless chargers. Despite the fact that when placed on a device, wireless chargers power the battery, a cable must still be used to connect the gadget to an electrical outlet.
Tesla thought that the earth and air were crucial tools for transmitting electricity at the time because they were excellent conductors of energy. Tesla said that by creating an electrical mesh between the earth and the air, the towers made it possible to use energy more readily. Tesla views the earth and the air as conductors, but since they act as insulators, wireless electrical transmission cannot occur through them.
-
Electricity Transmission with Tesla Coil
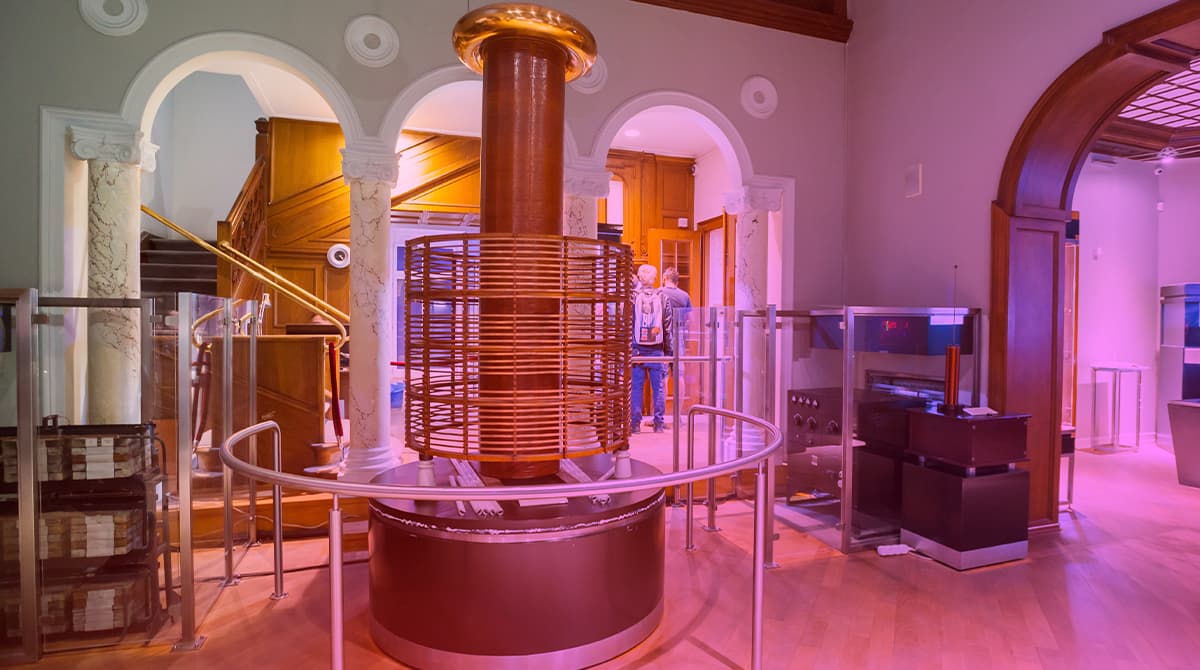 The Tesla coil was and continues to be groundbreaking because it can carry electricity wirelessly. In general, the Tesla coil can be described as a machine that produces extremely high voltages. The theories made possible by the Tesla coil also served as the basis for the technology employed in wireless data transfer.
The Tesla coil was and continues to be groundbreaking because it can carry electricity wirelessly. In general, the Tesla coil can be described as a machine that produces extremely high voltages. The theories made possible by the Tesla coil also served as the basis for the technology employed in wireless data transfer.
In its simplest form, the Tesla coil converts an electric current into voltage. A shifting magnetic field can be released thanks to this voltage. Electricity is produced by the magnetic field's fluctuation. In other words, it enables a nearby lamp to operate and provide light. A lamp placed next to the Tesla coil may light up the area surrounding it even without a plug.
How then does this coil function?
The lamp is able to light up because the Tesla coil produces an electric current that passes electrons into the lightbulb. This idea is similar to how our home lamps work, except that those lamps need wires to illuminate their surroundings and connections to supply them with the energy they require.
If you ask yourself, How does electricity get into our homes? you will find that Tesla's dream is still a long way from being achieved. However, approaches for wireless power transmission bring significant advancements to this area.
-
Techniques for Transmitting Electricity Wirelessly
There are several different methods for transmitting wireless electricity. What are these methods and are there real world applications?
When the receiver and transmitter are close to one another, inductively coupled power transmission is recommended. The most well-known uses include wireless device charging and electric toothbrush charging stations. For instance, if you have the right phone, you can start charging it as soon as you put it in the wireless charging station. This technique does away with the need for electric cables.
Microwave energy transmission is another important method. It allows for the transmission of energy over greater distances. Through the use of a transmitting antenna, microwave devices are utilized to transform electromagnetic energy into electrical energy. Then adjustments, filters, and other conversions are made. This strategy has many advantages, including high environmental compatibility. For the Internet of Things, or IoT, which is crucial to manufacturing, microwave energy transmission is crucial.
Light waves are another means of transferring power. Because they can be integrated into tiny devices, lights or lasers are more practical to utilize. However, as distance grows, transmission slows.
Inductive resonance coupling is one of the techniques that has recently been studied. It utilizes the magnetic resonance logic. There is a greater range of transmission than with inductively coupled power transfer.
When two objects have the same resonance frequency, they can efficiently transmit power. The basis of resonant inductively coupled energy transfer is based on the fact that objects are brought to the same frequency to make the energy transfer happen.
Inductively coupled power transmission is the most widely used technology in near-field applications. Microwaves and light waves are among the technologies of far-field wireless power transmission. These tools are prevalent in many aspects of daily life.
Application Areas for Wirelessly Transmitted Power
Wireless power transmission is now utilized in numerous areas, despite the fact that it cannot yet reach the degree that Tesla had in mind. These are the following application areas in general:
- One usage for this technology in daily life is wireless charging pads that may be used to power smartphones or smartwatches. Although smart devices need to be placed on a pad to charge, the phones' battery is charged wirelessly via these stations.
- Wireless power transmission is also used in the automotive industry.
- In the healthcare sector, medical products such as pacemakers have been charged inside the body via wireless power transmission for many years.
- There are plans to establish a solar power station on the moon and send the energy produced there to the earth in the future using wireless power transmission technologies.
- According to the data, the market size of wireless power transmission is $10,111 billion in 2020, while this share is expected to increase to $26,663 billion by 2027 due to the increasing demand and the comforts it brings.
Hindrances to Wireless Power Transmission
Today, power can only be transmitted over short distances; for example, chargers such as for smartphones can only charge when in contact with each other. When contact is broken, energy transfer is halted.
Unlike envisioned by Tesla, it is not feasible to wirelessly power all cities due to energy losses and because efficiency declines with distance.
By generating magnetic fields, it is possible to circulate electricity in the air and use it wirelessly, but this system typically only functions in close proximity. Up to a certain limit, electricity can be transmitted over vast distances using light waves, but the efficiency is quite low.
If Tesla's concept for wireless power transfer came to fruition, you could currently charge your smartphone while jogging down the street at no cost.
Do you think Tesla's dream of wireless electricity is possible in the near future? You can share your ideas with us in the comments.

 Online Services
Online Services Application Inquiry
Application Inquiry Pay Assurance Fee
Pay Assurance Fee Query Installation Number
Query Installation Number Compensation Fee Inquiry
Compensation Fee Inquiry Automatic Payment Order Inquiry
Automatic Payment Order Inquiry Partnership
Partnership







Leave a Comment
Comments (1)
A
Anthony Bailey
I think wireless electricity is the future and if it and if it isn't what it is there's nothing left to explore except for failure what what other frontier is there I think we should ground ourselves and get ready for the next wave