What is the Joule? Energy Units and Their Uses
What is in this article?
Energy is at the basis of all physical phenomena in the universe. Understanding this concept, which we encounter in different states such as kinetic, potential, heat, electrical and chemical energy, enables us to interpret the world more accurately both in daily life and in scientific studies. The Joule, which is used to measure energy, is one of the basic units of measurement that brings different types of energy to a common denominator.
In this article, we discuss in detail what the joule, a unit that is frequently used in energy measurement, is, how it is calculated, its fields of use and its relationship with energy efficiency.
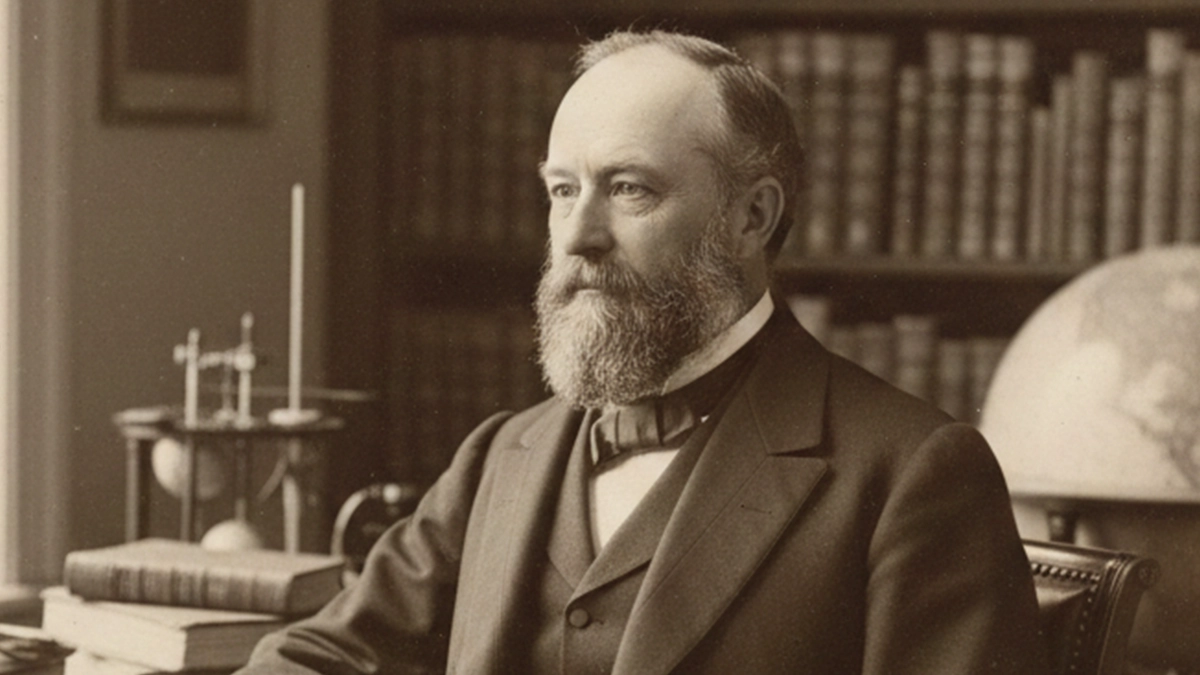 This unit of energy is named after the famous British physicist James Prescott Joule to honor his work on energy, especially thermodynamics and thermal energy. Let's take a closer look at the energy unit joule.
This unit of energy is named after the famous British physicist James Prescott Joule to honor his work on energy, especially thermodynamics and thermal energy. Let's take a closer look at the energy unit joule.
What is the Joule? Definition and History
The Joule (J) is the basic unit of energy of the International System of Units (SI) used to measure energy, work and heat. It refers to the amount of energy released by a force exerted on an object and is widely used in electrical, mechanical and thermal systems.
This definition makes it clear why the joule is used as a common unit of measurement across different fields of physics. The joule, denoted by (J), can be expressed in different ways. The work done by moving an object for a meter with 1 newton of force is expressed as 1 joule. Also, the energy generated as heat when an electrical current of 1 ampere passes through a resistance of 1 ohm is 1 joule. In other words, the amount of energy that a 1-watt power supply gives off in one second (1 watt-second) is 1 joule. For the unit joule that is used to measure thermal energy, 1 calorie of heat equals 4.186 J.
Talking about the joule, one should mention the British physicist James Prescott Joule, the namesake of the unit. James Prescott Joule (1818 - 1889), is known for his studies on the relationship between heat and mechanical work. As a result of his work, the conservation of energy and the first law of thermodynamics were confirmed. His other studies helped to discover the fact that the electrical current passing through a resistance emits heat, a phenomenon that is known today as Joule's law.
 Joule's Significance in Physics and Energy
Joule's Significance in Physics and Energy
The concept of joule is used in many different fields in physics and has a very wide range of uses. The joule is used to express different types of energy such as potential energy, kinetic energy, thermal energy, electricity and chemical energy. For this reason, the concept of joule is supported in various fields of physics, from the functioning of mechanical systems to the expression of thermal exchange in thermodynamic systems. This common use of the Joule provides the basis for a standardized and consistent comparison and calculation in physics.
The Joule in Mechanical Systems
As far as mechanical systems are considered, you can understand the transformation of energy in a much better way thanks to the concept of joule. The work done in mechanical systems can be against gravity or for different purposes, such as compressing a spring. The Joule is used to denote all this work done and energy expended.
Joule in Thermodynamics
In thermodynamics, the concept of joule helps to express heat transfer and energy exchange in the processes of heating and cooling substances. This allows physicists to make calculations based on the first law of thermodynamics while conducting consistent studies on the thermal properties of matter.
Joule in Electricity
One of the fields where the concept of Joule is widely used is electricity. It has a wide range of uses, from calculating the electricity stored in a system to evaluating energy efficiency. In this sense, the joule creates a common measurement language between different disciplines in physics.
Calculation and Conversion Formulas for Joule
The fact that the joule is a derived unit means that it can be determined by calculations based on measurements made in different units. In order to find the value of joule, which expresses energy, one has to use some formulas. The basic formula used to calculate in joule is as follows:
Joule = m . N = m x kg x m / s2 = m2 x kg / s2
Calculating the Joule through Work and Force
- To find the work done in joules, you need to know the force applied in newtons and the distance in meters traveled as a result of the force applied. Then you can calculate the work done in joules using the following formula:
Work (joule) = Force (newton) x Distance (meter)
Calculating the Joule in Electricity
- The Joule also expresses electricity. To calculate the energy in any electrical circuit, you need the power in watts and time in seconds. Then you can calculate the energy in joules using the following formula.
- Energy (joules) = Power (watts) x Time (seconds)
Calculating Kinetic Energy
- When the kinetic energy is to be calculated in joules, the following formula can be applied using the mass in weight and the velocity in m/s.
Kinetic Energy (joule) = ½ x Mass (kilogram) x Velocity2
= ½ x Mass (kilogram) x (meters per second)
Calculating Heat and Temperature Change
- Temperature change can also be expressed in joules. To calculate this, you need the mass in kilograms as well as the temperature change in Celsius or Kelvin. You also need the specific heat capacity value, which is a constant that varies depending on the matter. Then the temperature change in joules can be calculated by applying the following formula.
Temperature Change (joule) = Mass (kilogram) x Specific Heat Capacity (c) x Temperature Change (oC, K)
Unit Conversions of Joule
The Joule can be converted into different units of energy. The most common conversions are as follows:
- 1 kilowatt-hour (kWh) = 3,600,000 joules
- 1 calorie (cal) = 4.181 joules
- 1 BTU = 1,055 joules
 Conversion of Values in Joule
Conversion of Values in Joule
It is possible to convert energy in joule into many units such as watts, calories, BTUs or kWh. However, you can get healthier and more accurate results by using applications developed specifically for joule conversion. The joule equivalents of the most commonly used related units are as follows:
- 1 kilowatt-hour (kWh) = 3.6 million joules
- 1 calorie (cal) = 4.181 joules
- 1 British Thermal Unit (BTU) = 1055 joules
Basic Concepts Related to Joule
To understand the concept of the Joule better, you should have sufficient knowledge about other related concepts. Let's start with the concept of work. The work in question here is the energy transfer that occurs as a result of moving an object over a certain distance under the influence of an external force. Work can be found by multiplying force and displacement.
One joule represents the work done when a force of 1 newton displaces an object by 1 meter in the direction of the force applied. In short, 1 joule is equal to 1 newton-meter. Newton is the SI unit used to express force. It expresses the force required to move 1 kilogram of mass at a speed of 1 meter/second.
In thermodynamics, the joule is used to express heat transfer and energy exchange. At this point, another concept you may encounter is calories. The energy unit used to measure heat, calorie is the amount of energy required to increase the temperature of 1 gram of water by 1 degree Celsius. Its joule equivalent is 4.181 J.
In addition to mechanical systems and thermodynamics, the joule is also used to express electricity. In electrical systems, power is measured in watts. 1 joule is the amount of energy transferred by 1 watt in 1 second.
Uses of Joule in Daily Life
You may have never used the joule in daily life. Nevertheless, you should keep in mind that the joule is used in energy calculations across many fields. Especially if you look at the nutritional values on the back of packaged foods, you may come across values in kcal and KJ. Also, here are some interesting examples of the use of joules of energy in daily life:
-
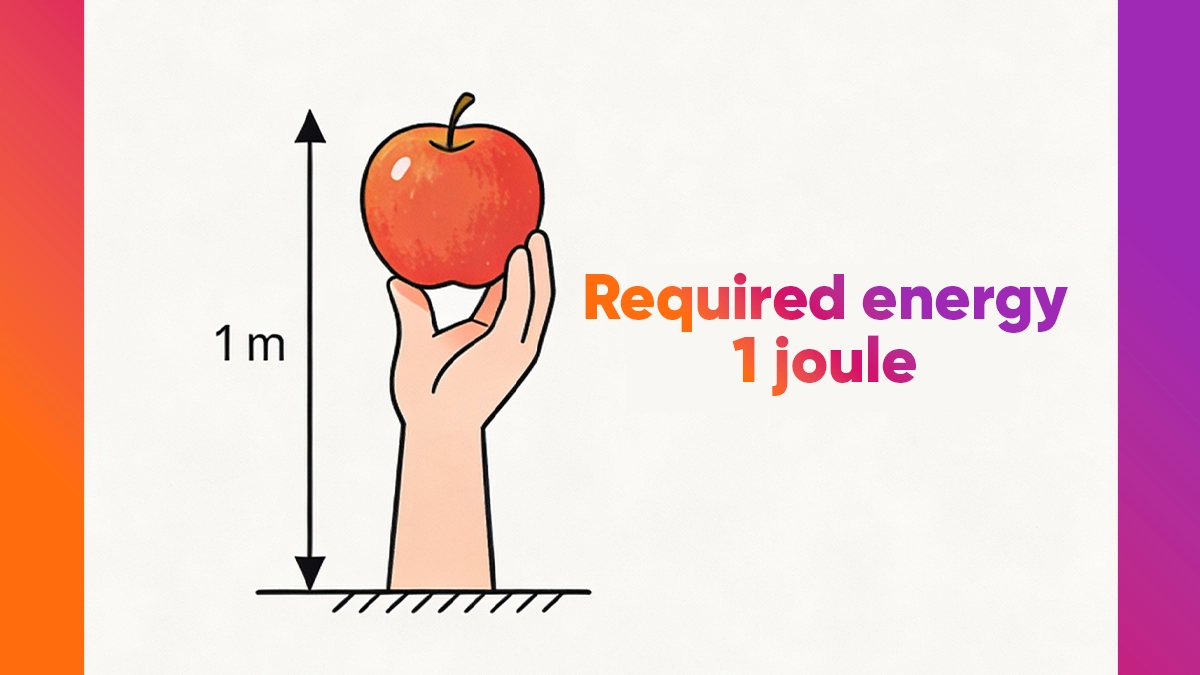
The energy required to lift an average-sized apple or tomato 1 meter above the ground is 1 joule.
-
It takes 1 joule of energy to light a 1-watt LED for 1 second.
-
It takes approximately 1 joule of energy to take a glass of water from the table and bring it to your mouth.
-
The heat required to raise the temperature of one gram of water from 0oC to 1oC is 4,184 joules.
-
The kinetic energy of a ball thrown by a professional baseball pitcher is approximately 230 joules.
-
The combustion of just one gram of gasoline in air releases 50 kJ of energy.
 Monitoring the Joule in Energy Efficiency
Monitoring the Joule in Energy Efficiency
One of the hot topics in energy use today is energy efficiency. Energy efficiency aims to perform a given task by consuming much less energy. It can provide economic savings by minimizing energy consumption as well as ensuring environmental sustainability.
Energy efficiency has many environmental impacts, from reducing the need for fossil fuels to providing strength in the fight against climate change. However, this impact is not limited to the environment. Thanks to energy efficiency, energy costs can be reduced to much lower levels. This has a positive impact on the budgets of individual users while it means creating resources for research and development or other fields for businesses. In this way, businesses can create their own opportunities for growth.
The relationship between energy efficiency and the joule arises when calculating consumption and loss of energy. In order to achieve energy efficiency in a system, it is necessary to know where exactly the energy goes to. It should be possible to calculate how much of the energy can be used and how much should be considered as loss.
To calculate energy efficiency as a percentage, one needs to divide the energy output by the energy input. Thus, you can calculate your energy efficiency ratio. To express this value as a percentage, simply multiply it by 100.
- Energy Efficiency = Energy Output / Energy Input
- %Energy Efficiency = Energy Output / Energy Input x 100
You can apply energy efficiency measurement to a single device or an entire system. Consider this example:
Let's assume that an equipment in a factory gives an output of 300 joules for an input of 500 joules. The calculation should be as follows:
Energy Efficiency = 300 / 500 x 100 = 60% efficiency. So, the energy efficiency of the equipment is 60%.
So where does the loss in energy occur? In electrical systems, most of the energy is lost as heat. You can experience this in the fact that the electrical appliances and light bulbs you use heat up over time. In light bulbs also known as incandescent or filament bulbs, 10 out of every 100 joules of energy consumed is converted into light, while 90 is dissipated as heat. A quick calculation shows that you can calculate the efficiency of an incandescent light bulb in the example as 10%. In other words, it means that you waste 9 out of every 10 Turkish lira spent on lighting. This shows the impact of energy inefficient devices on the environment and the economy.
The energy unit joule is a concept frequently used in calculating energy efficiency. So, are you taking steps towards energy efficiency in your home or workplace? Don't forget to share your thoughts with us in the comments.

 Online Services
Online Services Application Inquiry
Application Inquiry Pay Assurance Fee
Pay Assurance Fee Query Installation Number
Query Installation Number Compensation Fee Inquiry
Compensation Fee Inquiry Automatic Payment Order Inquiry
Automatic Payment Order Inquiry Partnership
Partnership

Leave a Comment