
What is a Power Grid? National System Structure
What is in this article?
Electricity is one of the most fundamental necessities of modern life. Pulling your phone out of the charger when you wake up in the morning, making your coffee, or lighting up your home in the evening has become so ordinary that you often do not think about the massive system at work. However, electricity travels a long way from power plants to our houses.
At the heart of this journey is the power grid. So how does this system work? What stages does electricity go through from generation to distribution? The rest of the article will give you a closer look at the structure and operating principle of the grid system
.
.webp) What is a Power Grid? Basic Concepts and Definitions
What is a Power Grid? Basic Concepts and Definitions
Electricity goes through a very complex system from being generated at the source to powering your devices. The system that manages the whole process is called a power grid. A power grid is a large-scale infrastructure that enables power to flow from generation to consumers. It is not made up exclusively of generation plants but it also includes power transmission lines, distribution networks and balancing systems.
The first stage of the power grid is the power plants where electricity is generated. These plants generate electricity using various fuels. Each power plant system supplies a certain capacity of electricity to the grid. For example, large hydroelectric power plants can generate hundreds of megawatts of electricity, while a small wind farm can provide electricity at low capacity.
High-voltage electricity from transmission lines is transformed to low voltage levels at transformer substations. This makes the electricity suitable for the distribution network. Substations are critical to the stability of a grid. Any disruption in the conversion process has very dangerous consequences.
The power grid is a dynamic system that must be constantly kept in balance. The amount of electricity generated and the amount of electricity consumed should always be kept in balance. The balance is maintained by energy management systems (EMS) and automatic control systems. These systems adjust generation according to demand and maintain the stability of the grid to prevent potential outages.
Types and Characteristics of Power Grids
Power grids are an essential part of modern life. Whether it is high-voltage lines running from large-scale power plants to urban distribution or the everyday electricity infrastructure you use at home, they are all part of an interconnected system. Basically, grids are categorized by the way energy is transmitted and voltage by intended use. Each system has its own limitations. A transmission grid transmits the high-voltage power generated in power plants over long distances, while a distribution grid lowers the voltage and spreads the electricity across urban grids, delivering it to the end user.
Grids also differ by their intended use. Industrial grids established specifically for large-scale industrial facilities, commercial grids serving commercial enterprises and residential grids meeting daily needs of individual users are the main examples of this classification.
Alternating current (AC) and direct current (DC) grids are differentiated according to the way electricity is transmitted. Today's urban power grids mostly use alternating current, while renewable energy sources such as battery systems and solar panels operate on direct current.
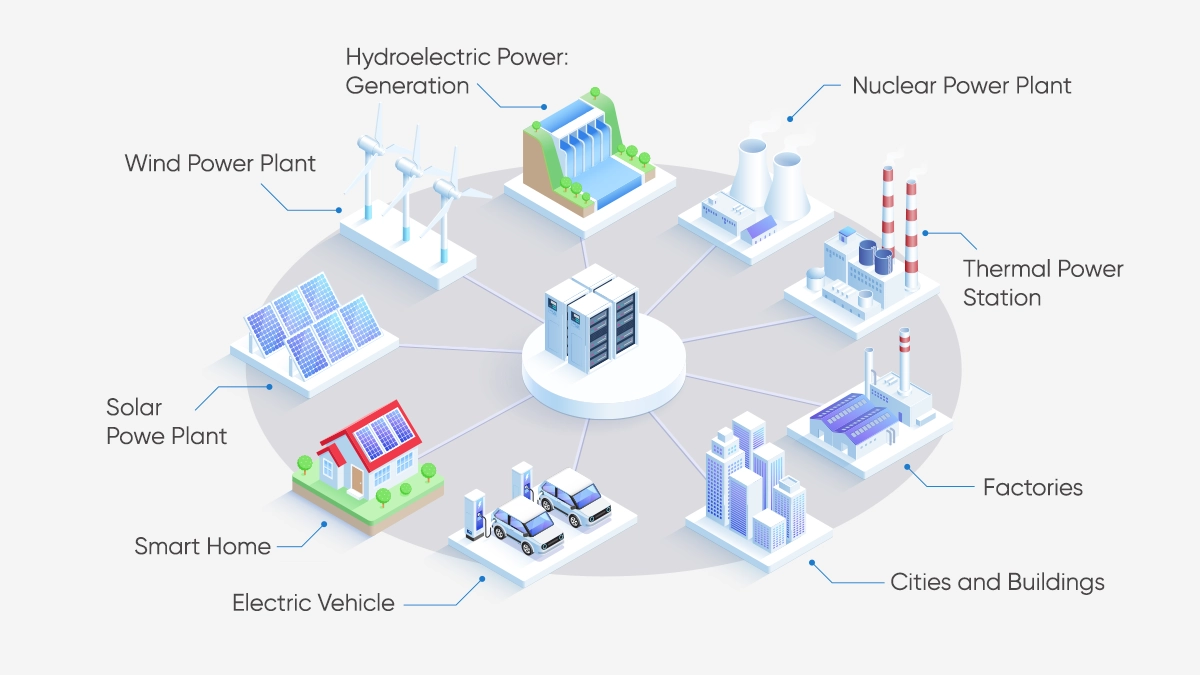 Basic Components of National Power Grid
Basic Components of National Power Grid
Modern power grids are designed for the continuous transmission of energy. In order to understand how a power grid works, one should look at some concepts related to electricity:
Power Generation
Electricity is not a readily available source of energy. It has to be generated by various means. Today, the sources used for power generation today are mainly as follows:
-
Thermal Power Plants: Fossil fuels such as coal, natural gas or oil are burned to get water vapor, which is used to turn turbines to generate electricity.
-
Hydroelectric Power Plants: They generate electricity using the force of water. Türkiye very rich in hydroelectric power plants.
-
Wind Power: Wind turbines convert the kinetic energy of air flow into electricity.
-
Solar Power: Solar panels convert sunlight directly into electricity through photovoltaic cells.
-
Nuclear Power Plants: The fission of radioactive elements such as uranium releases a large amount of energy. The resulting energy is used to produce steam, which is used to turn turbines.
Power Transmission
Once power is generated, it cannot be supplied directly to the consumer. This is mainly because of the loss of energy due to resistance during the transmission of power. In order to minimize the losses, power is transmitted over long distances by turning up the voltage to much higher levels.
The electricity is transmitted at high voltage levels such as 154 kV or 380 kV after it is generated. High voltage lines provide intercity or international power transmission. Electricity can be transmitted even over thousands of kilometers through such lines. In the transmission process, substations control the voltage, lowering or raising it as needed.
Electricity transmission is part of a larger system called the national power grid. The national grid of Türkiye is managed by TEİAŞ (Türkiye Electricity Transmission Corporation) to provide uninterrupted power to every part of the country.
Power Distribution
Once power transmission lines have delivered the power to large city centers or industrial zones, the power should be made available for the use of end consumers. This is where the distribution grid comes into play. Power distribution goes through the following stages:
-
High-voltage electricity from transmission lines is routed to local substations.
-
At the substations, the voltage is reduced to a level that is suitable for use in residential areas.
-
In Türkiye, electricity is distributed by regional distribution companies. It is transmitted to neighborhoods, streets and then to buildings via local distribution lines. Electricity entering the buildings reaches the power sockets.
Electricity Frequency and Voltage Levels
The safe use of electricity relies on certain standards. Key standards involve frequency and voltage levels. The frequency of the power grid used in Türkiye is 50 Hz. This indicates how many times the electric current changes direction each second.
Voltage levels are divided into 3 categories: high, medium and low. The high voltage used on transmission lines has to be above 154 kV. On urban distribution lines, 36 kV is used. In areas reaching the end user, distribution occurs at a standard 220 Volts.
Electricity Transmission Lines and Distribution Systems
Electricity goes through a complex journey from the point of generation to the point it reaches consumers. It reaches your home through electricity distribution systems, aerial lines and underground cables. While aerial lines are predominantly preferred in rural areas, underground cables are more commonly used in populated areas within the city for aesthetic concerns.
In recent years, smart grid technologies have made power distribution systems more efficient and reliable. Features such as remote management allow electricity consumption to be controlled more effectively. Transmission and distribution systems are continuously upgraded to provide uninterrupted power as a fundamental element of modern life. Improvements in technological infrastructure are intended to reduce losses in energy and create a more sustainable system.
Grid Security and Protective Measures
Some measures are mandatory to protect a power grid against risks such as failures, natural disasters or cyber-attacks. Measures taken to ensure the physical security of the power grid are intended to prevent damages to the grid. Transformer substations are protected by security cameras, alarms and barriers. Only authorized personnel have access to the critical components of the power grid. Structures are reinforced against natural disasters such as floods, earthquakes or storms.
.webp) Various automation systems are used to quickly detect and resolve failures in the power grid. When a failures occurs, the grid automatically isolates the failed area and ensures that the other parts of the grid remain up. Protection relays prevent outages by detecting abnormal changes in electric current. SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) systems are used to monitor and manage the grid status instantaneously.
Various automation systems are used to quickly detect and resolve failures in the power grid. When a failures occurs, the grid automatically isolates the failed area and ensures that the other parts of the grid remain up. Protection relays prevent outages by detecting abnormal changes in electric current. SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) systems are used to monitor and manage the grid status instantaneously.
The integration of power grids with digital systems may also make them vulnerable to cyber-attacks. For this reason, cyber security measures are critical for grids. Networks connected to a power grid must be protected with strong security protocols.
Continuous monitoring is carried out to detect potential cyber attacks on the grid. The infrastructure is supported by backup systems so that it can be quickly recovered in the event of a possible cyber attack or data loss.
For the uninterrupted operation of the power grid, it is necessary to utilize alternate sources of energy and be prepared for potential emergencies. Power generators and other power storage systems are installed in national power grids for use in emergencies. Power storage systems increase the flexibility of the grid and ensure that power can be supplied quickly when the demand surges. Demand and supply are monitored and directed to maintain the balance between the generation and consumption of electricity.
 Smart Grid Technologies and Future
Smart Grid Technologies and Future
Smart grid technologies are advanced technologies that enable power grids to operate more efficiently. These technologies enable the digitalization of grids and more efficient management of power generation and consumption. Smart meters measure power consumption instantaneously and transmit that data digitally, allowing operators to monitor power consumption accurately. They make power consumption more transparent, enabling power prices to be set dynamically.
Smart grids respond to fluctuations in power demand using demand response technologies. You can reduce your power bills by shifting your consumption to the periods of lower demand. This helps to manage the grid more efficiently when the demand surges.
Power storage systems are especially critical for more efficient use of renewable energy sources. Renewable energy sources such as wind and solar generate power at certain hours but this may not coincide with the time of peak demand. Storage systems store excess power so that it can be released when needed.
Smart grids make grid management more efficient by means of data analytics and artificial intelligence. Real-time data analysis optimizes power consumption, predicts failures and accurately determines energy prices. Artificial intelligence will allow grids to manage themselves and automate processes such as fault detection. It can also analyze power consumption habits of users to encourage more efficient energy use.
As part of smart grid technologies, IoT (Internet of Things) devices enable a continuous flow of data between parties. This technology helps the grid to react more smartly. All devices communicate with each other, improving energy efficiency and facilitating failure management.
Smart grids are a important tools for reducing carbon emissions and protecting the environment. Integrating renewable energy sources and optimizing power consumption will make a grid more sustainable. Reducing the carbon footprint helps to minimize environmental impacts. Smart grids will make energy use more sustainable and greatly reduce carbon emissions globally.
Making the basis of the energy infrastructure of the future, smart grid technologies offer a more reliable and efficient system for users and energy providers alike. In this transformation process, it is critical for consumers to consciously manage their power usage habits. Aydem Perakende empowers its customers to adapt to this transformation with transparent consumption monitoring, various tariff options, digital means of transaction and informational services on energy saving. You can also benefit from the advantages offered by Aydem Retail to use power more efficiently and step into the energy world of the future with confidence.

 Online Services
Online Services Application Inquiry
Application Inquiry Pay Assurance Fee
Pay Assurance Fee Query Installation Number
Query Installation Number Compensation Fee Inquiry
Compensation Fee Inquiry Automatic Payment Order Inquiry
Automatic Payment Order Inquiry Partnership
Partnership

.webp)





Leave a Comment